Article contents
Analysis of the methods to calculate austenite static recrystallization volume fraction
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 13 June 2016
Abstract
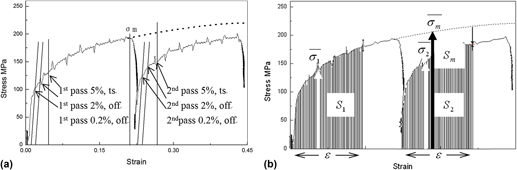
Double deformation technique is often used to study static recrystallization (SRX) behavior of materials, and SRX volume fraction can be calculated by the analysis of the stress–strain curve from this technique. The suggested methods to analyze the curve are different, which may lead to different results or even large deviation. In the present research, the methods were discussed based on the stress–strain curves from double deformation compression tests. The results showed that 2% offset method agrees well with 5% total strain method and they can give a better evaluation of SRX volume fraction for the tested steel in the absence of precipitates. While the results from 2% offset or 5% total strain method deviate from the ones from area measurement method when precipitation occurs. Therefore, area measurement method is more suitable when precipitates play a role in SRX process. However, the strain should be large enough to perform this method.
Keywords
- Type
- Articles
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Materials Research Society 2016
Footnotes
Contributing Editor: Yang-T. Cheng
References
REFERENCES
- 7
- Cited by



