Published online by Cambridge University Press: 28 September 2012
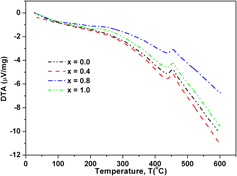
The structural and magnetic properties of the Al cosubstituted cubic spinel ferrite series MgAlxFe2−xO4 (x = 0.0, 0.4, 0.8, and 1.0) synthesized through a coprecipitation method were characterized by means of x-ray powder diffraction, infrared (IR) spectroscopy, transmission electron microscopy (TEM), differential thermal analyses, and vibrating sample magnetometer. Lattice constants determined from x-ray diffraction (XRD) measurements exhibit a decrease with increasingAl3+ ions in the ferrites system. The particle size using TEM was ∼33 nm for magnesium ferrite, which is in good agreement with values obtained by XRD method. The crystallization spinel formation for the parent ferriteMgFe2O4 using differential thermal analysis (DTA) technique was 454 °C. The two main bands observed in the IR spectra (tetrahedral and octahedral) were in the range (568–628 cm−1) and (431–460 cm−1), respectively. Magnetization curve shows the highest value for the sample with concentration x = 0.4.