Article contents
Preparation of porous zirconium microspheres by magnesiothermic reduction and their microstructural characteristics
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 09 August 2011
Abstract
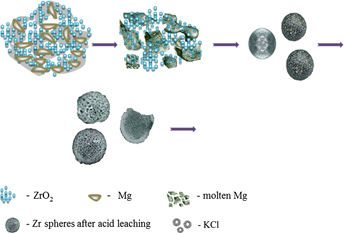
Porous zirconium metal microspheres were synthesized successfully by a combustion technique using ZrO2 + 2Mg starting mixture. In this process, a controlled amount of KClO3 + 3Mg is mixed with ZrO2 + 2Mg to enable a self-sustaining combustion process and to promote a reduction of the ZrO2. The framework structure, morphology, and porosity of zirconium microspheres were determined using various techniques. Microscopic visualization suggested that the spherical structure has macroporous windows of diameter ∼0.5–5.0 μm and the space between the macropores has a wormhole-like mesoporous/microporous structure. The mesoporous structure had a pore diameter of ∼1.19 nm. This procedure provides an easy method for the synthesis of porous microspherical assemblies of Zr composed of submicrometer size particles.
- Type
- Articles
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Materials Research Society 2011
References
REFERENCES
- 3
- Cited by


