Article contents
Nanotribology of clean and modified gold surfaces
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 07 May 2013
Abstract
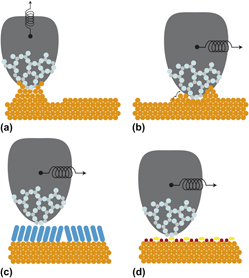
Gold surfaces exhibit most interesting frictional properties on the nanometer scale. They can be studied in detail by means of friction force microscopy. Atomic-scale variations of the lateral force allow investigation of microscopic mechanisms of sliding. Friction force microscopy even reveals surface reconstruction of the gold surface as a modulation of the lateral force signal. Experiments indicate that the mobility of surface atoms at room temperature and plastic deformation mechanisms give rise to neck formation between gold and microscopic asperities in sliding contact. The frictional properties of gold surfaces change dramatically at temperatures below 150 K, where the surface diffusion is greatly reduced. Insight into the lubrication properties of self-assembled monolayers is provided by molecular-scale modulations of frictional forces. Molecular-scale maps of the friction force also allow identification of the relevant surface structure in experiments on electrochemically modified gold surfaces. Variation of the electrochemical potential is a means to reversibly switch between low and high friction states on gold surfaces.
- Type
- Invited Feature Paper
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Materials Research Society 2013
References
REFERENCES
- 14
- Cited by


