Article contents
Large effect of structural variations in the columnar silicon electrode on energy storage capacity and electrode structural integrity in Li-ion cells
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 07 October 2020
Abstract
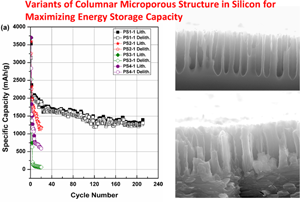
Silicon electrodes with the columnar macroporous structure were investigated to determine the effect of variations in the columnar pore morphology on lithiation and energy storage capacity in Li-ion cells. Several variants of macroporous Si columnar electrodes were electrochemically cycled against the Li reference electrode. The changes in macro-pore size and Si wall thickness of the columnar architecture greatly affected the cyclic Li storage and discharge capacities. A strong correlation of the Li-storage capacity with the ratio of Si wall thickness to pore diameter is found to exist. Specifically, one columnar Si electrode with an optimum macroporous structure exhibited a very high reversible specific capacity of ~1250 mAh/g (total capacity 1.2 mAh/cm2) for over 200 cycles. Electron microscopy revealed that the high reversible Li-storage capacity is due to the macropores accommodating the change in volume of lithiation and providing nearly complete reconstruction of Si walls upon delithiation. The present observations can lead to practical, high-capacity, and damage-resistant Si electrodes for Li-ion batteries.
- Type
- Article
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © The Author(s), 2020, published on behalf of Materials Research Society by Cambridge University Press
References
- 6
- Cited by



