Published online by Cambridge University Press: 29 April 2019
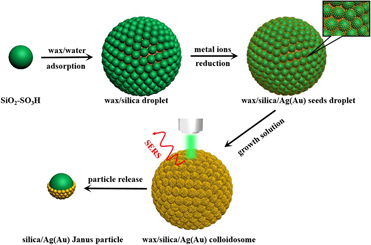
Noble metal (Ag, Au) nanoparticles (NPs) deposited on the surface of three-dimensional (3D) materials are promising 3D surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) substrates. In this work, the authors reported the preparation of 3D wax/silica/Ag(Au) colloidosomes by sulfonic acid group–terminated silica spheres (SiO2–SO3H) combined with a Pickering emulsion technique, as well as seed-mediated growth method of noble metal NPs. The presence of –SO3H group on the silica spheres not only improves significantly the quality of wax/silica colloidosomes (forming perfect silica shell around wax droplet) but also can adsorb metal precursor ions via electrostatic attraction for further growth of metal NPs. The size and coverage of Ag(Au) NPs on wax/silica droplets can be facilely tuned, and relevant wax/silica/Ag(Au) colloidosomes and silica/Ag(Au) Janus particles are obtained via this strategy. The obtained wax/silica/Ag colloidosomes as 3D SERS substrates exhibited excellent SERS enhancement ability and detection limit of 4-aminothiophenol reached 10−9 M.