Article contents
Effect of Ta2O5 addition on the electrical and magnetic properties of nanocrystalline MgCuZn ferrites
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 12 September 2014
Abstract
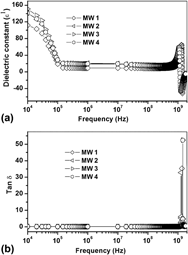
Ta2O5 added MgCuZn ferrites are prepared by the microwave-hydrothermal (M-H) processing. The nanocrystalline ferrites are sintered to a temperature of 900 °C using conventional sintering (CS) and microwave sintering (MW) methods. The effect of Ta2O5 addition on the microstructure, d.c. resistivity, and Curie temperature of the ferrites has been studied. By the addition of Ta2O5 to MgCuZn ferrites, resistivity decreases without grain growth. The complex permittivity and complex permeability of the prepared samples were measured in the frequency range from 10 kHz to 1.8 GHz. The value of ε′ and tan δ for all the samples decreases from 10 to 100 kHz and almost remains constant up to 300 MHz and increases further by increasing the frequency up to 1 GHz. The µ* spectra are analyzed into two magnetization processes with a focus on the grain size of the ferrite samples. The present ferrites exhibited high values of permeability (>1000) in the frequency range of 10 kHz to 50 MHz. Then the values of permeability are found to decrease with an increase in frequency up to 180 MHz and finally, frequency dispersion occurred at 200 MHz.
- Type
- Articles
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Materials Research Society 2014
References
REFERENCES
- 9
- Cited by


