Article contents
The effect of radio frequency power on the structural and optical properties of a-C:H films prepared by PECVD
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 16 January 2017
Abstract
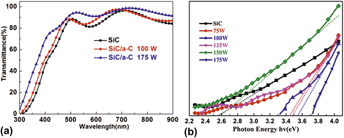
Hydrogenated amorphous carbon (a-C:H) films with a designed buffer layer of amorphous hydrogenated silicon carbide on the substrates were fabricated by plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition (PECVD). The effect of radio frequency (RF) power on the structural and optical properties of a-C:H films was investigated. The ratios of sp 3 to sp 2 of carbon atoms and hydrogen contents in the RF power range of 75–175 W are determined and a similar trend as a function of power. The increase of sp 3 to sp 2 ratio leads to the increase of transmittance and optical gap of a-C:H films. a-C:H film under an RF power of 175 W possesses high transmissive ability (>80%) in the visible wave length, even the highest transmittance value of about 94.2% is achieved at the wave length 550 nm. These results show the optimal a-C:H films which are promising for the applications in the area of solar cells acting a window layer and antireflection layer.
- Type
- Articles
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Materials Research Society 2017
Footnotes
Contributing Editor: Mauricio Terrones
References
REFERENCES
- 9
- Cited by



