Published online by Cambridge University Press: 08 November 2011
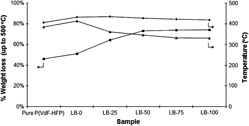
Solid polymer electrolytes (SPEs) with poly(vinylidene fluoride-hexafluoropropylene) [P(VdF-HFP)] as polymer host, doped with lithium trifluoromethanesulfonate (LiTf) and 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium trifluoromethanesulfonate (BMIMTf) have been synthesized via solution casting method. This P(VdF-HFP)/LiTf/BMIMTf-based SPE achieves ∼2.4 × 10−3 and ∼1.1 × 10−2 S·cm−1 at 30 and 80 °C, respectively, with 100 part by weight of BMIMTf incorporated into the system. A very interesting trend of temperature-dependence ionic conductivity has been obtained. A rationalization of the trend is given and the morphological changes observed in scanning electron micrographs seem to be commensurate with it. Thermogravimetric and differential thermogravimetric analyses reveal some changes in thermal properties of the SPEs, including the possibility of phase separation happening in the sample.