Introduction
The genus Stilestrongylus Freitas, Lent & Almeida, 1937, belongs to the family Heligmonellidae and the subfamily Nippostrongylinae (Durette-Desset, Reference Durette-Desset1971). Currently, 23 species are recognized in this genus, 21 of which are parasites of cricetid rodents, one of murids and one of echimyds (Digiani & Durette-Desset, Reference Digiani and Durette-Desset2007; Digiani et al., Reference Digiani, Navone and Durette-Desset2007; Souza et al., Reference Souza, Digiani, Simões, Luque, Rodrigues-Silva and Maldonado2009). The main taxonomic characteristics used to identify the genus Stilestrongylus are its dissymmetrical caudal bursa, its hypertrophied genital cone, and the number of ridges and the degree of inclination and orientation of the synlophe (Durette-Desset & Digiani, Reference Durette-Desset and Digiani2005, Reference Durette-Desset and Digiani2012).
Here we describe a new species of Stilestrongylus (Heligmosomoidea: Heligmonellidae) found parasitizing russet rice rats Euryoryzomys russatus (Wagner, 1848) (syn. Oryzomys russatus) (Rodentia, Sigmodontinae) in the Atlantic Forest in the Serra do Tabuleiro State Park, municipality of Santo Amaro da Imperatriz, Santa Catarina state, southern Brazil. The rice rats have terrestrial habits, feed on seeds, fruits and insects (Emmons & Feer, Reference Emmons and Feer1997) and inhabit south-eastern and southern Brazil, north-eastern Argentina and eastern Paraguay (Musser & Carleton, Reference Musser, Carleton, Wilson and Reeder2005). In Brazil, E. russatus occurs in the Atlantic Forest from Bahia to Rio Grande do Sul states, including eastern Minas Gerais state (Patton et al., Reference Patton, Pardiñas and D'Elía2015).
Materials and methods
Collection of nematodes
Twenty-eight specimens of E. russatus were collected at the Serra do Tabuleiro State Park (27°52′27″S, 48°49′26″W), a reserve of the Atlantic Forest of c. 84,130 ha. The rodents were captured in areas of Ombrophilous Dense Forest in October 2014 and May 2015 using Sherman and Tomahawk traps (H.B. Sherman traps, USA; Tomahawk Live Trap, USA) and pitfall traps made of buckets. Biosafety techniques and personal safety equipment were used during all procedures involving animal handling and biological sampling.
Morphological analysis
The rodents were euthanized and dissected for collection of helminths. The nematodes were collected from the small intestine, washed briefly in NaCl solution and fixed in hot AFA (2% acetic acid, 3% formaldehyde and 95% ethanol). Fifteen male and 10 female nematodes were cleared in lactophenol and examined for their morphological characteristics. Drawings were made using a Zeiss Standard 20 light microscope (Carl Zeiss AG, Germany) equipped with a lucid camera. The synlophe was studied in one male and one female, and the total number of dorsal and ventral ridges was counted according to Durette-Desset (Reference Durette-Desset1985) and Durette-Desset & Digiani (Reference Durette-Desset and Digiani2015). The terminology used here relating to the caudal bursa follows Durette-Desset & Digiani (Reference Durette-Desset and Digiani2012) and Durette-Desset et al. (Reference Durette-Desset, Digiani, Kilani and Geffard-Kuriyama2017). Measurements are given in micrometres (unless otherwise stated) for holotype or allotype specimens, followed by the range for paratypes, with the mean in parentheses. Holotype, allotype and paratype specimens were deposited in the Helminthological Collection of the Oswaldo Cruz Institute (CHIOC) at the Oswaldo Cruz Foundation, in Rio de Janeiro state, Brazil.
Results
Systematics
Heligmosomoidea Travassos, 1914
Heligmonellidae Leiper, 1912
Nippostrongylinae Durette-Desset, 1971
Stilestrongylus rolandoi n. sp.
Description
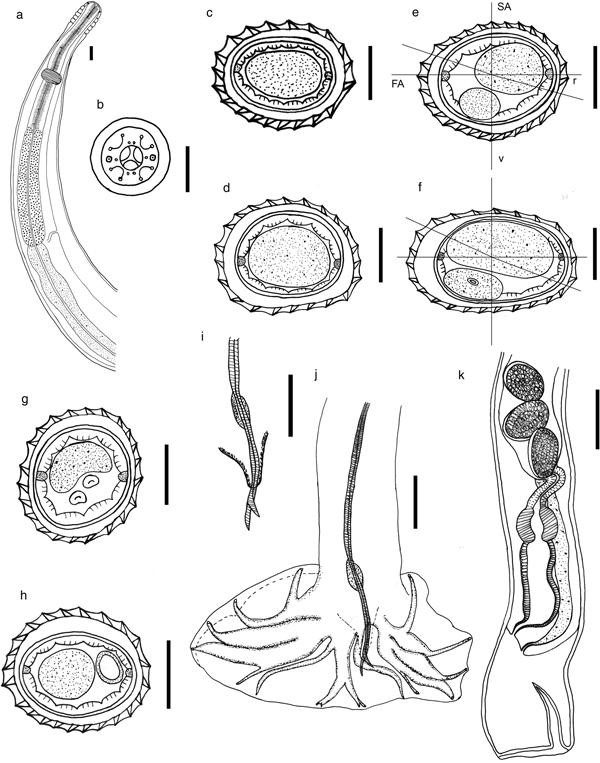
General. Small nematodes tightly coiled. Excretory pore located at posterior end of the oesophagus (fig. 1a). Cephalic vesicle present. Rounded mouth opening in apical view, surrounded by two amphids, six internal labial papillae, four external labial papillae and four submedian cephalic papillae (fig. 1b). Cuticle bearing longitudinal, uninterrupted ridges appearing posterior to cephalic vesicle, ending just anterior to caudal bursa in males and reaching posterior extremity in females. Synlophe with 20 ridges (nine dorsal and 11 ventral) in males (fig. 1c) and 22 (11 dorsal and 11 ventral) in females (fig. 1d) at level of the oesophago-intestinal junction; 27 ridges at mid-body (12/15) in males (fig. 1e) and 24 (10/14) in females (fig. 1f); 22 (11/11) anterior to caudal bursa in males (fig. 1g) and 23 (11/12) anterior to vulva in females (fig. 1h). Ridges at mid-body slightly unequal in size in both males and females, with smaller ridges oriented from ventral right to ventral left and from dorsal right quadrant to dorsal left. Ridges at mid-body positioned in double-axis orientation. In males, right axis inclined at 75° to sagittal axis and left axis at 75°. In females, right axis inclined at 65° to sagittal axis and left axis at 70°.

Fig. 1. Stilestrongylus rolandoi n. sp. (a) Anterior extremity, right lateral view, female. (b) Female, head, apical view. (c) Section through anterior body, posterior to oesophago-intestinal junction, male. (d) Section through anterior body, posterior to oesophago-intestinal junction, female. (e) Transverse section of body, at mid-body, male. (f) Transverse section of body, at mid-body, female. (g) Transverse section of body, male, just anterior to caudal bursa. (h) Transverse section of body, female, just anterior to vulva. (i) Male, genital cone. (j) Male, caudal bursa, ventral view. (k) Female, posterior extremity, left lateral view. Scale bar 50 μm. Abbreviations: r, right; v, ventral; SA, sagittal axis; FA, frontal axis.
Male (holotype and 14 paratypes). Length 4.08 [2.82–4.14 (3.42)] mm, n = 15, width at mid-body 90.7 [94.5–149.1 (117.5)], n = 15; cephalic vesicle 74 [68.8–98.5 (85.7)] long, n = 8, and 33.6 [28.4–37.6 (32.1)] wide, n = 8. Nerve ring (n = 5) 156.1 [139.7–162.5 (148.8)] and excretory pore (n = 4) 225.3 [313.6–338.7 (326.9)] from anterior end. Oesophagus 321 [305.1–333.5 (321.5)] long, n = 5. Dissymmetrical caudal bursa, with right lobe more strongly developed than left lobe (CB DS RL+), both of types 1–4. Ray 2 in right lobe shorter than ray 2 in left lobe. Rays 3, 4 and 5 emerging from a common trunk: rays 3 separating from rays 4 at the middle of the lateral trunk, rays 4 and 5 robust, bifurcating at distal third. Ray 6 small, arising at the same level of bifurcation as rays 3. Rays 8 arising dissymetrically on dorsal trunk, right ray more distally than left ray. Dorsal ray divided at distal third into two branches, each divided at the extremity into two subequal branches, rays 9 (external) slightly longer than rays 10 (internal). Spicules alate, equal in length, 943.4 [807.7–1080.2 (963.3)] long, n = 13; spicule length to body length ratio (SpL/BL) of 23 (21–33%). Gubernaculum present, 47.7 [42.3–55.8 (49.3)] long and 25.3 [18.1–33.8 (26.6)] wide, n = 9. Genital cone hypertrophied, 56.2 [54–72.2 (62.3)] long and 53.5 [46.5–58 (52.2)] wide, n = 8 (fig. 1i, j).
Female (allotype and nine paratypes). Length 5.38 [4.13–6.17 (5.02)] mm, 128.6 [105.5–126 (116.5)] mm wide at mid-body, n = 10. Cephalic vesicle 85.6 [61.2–111.7 (85.1)] long and 34.7 [30.0–42.1 (34.6)] wide, n = 10. Distance from anterior end to nerve ring and to excretory pore 192.6 [172.8–209.9 (184.9)], n = 6 and 458 [375.3–473.6 (430.7)], n = 3, respectively. Oesophagus 453 [370.4–458.3 (431.2)] long, n = 4 (fig. 1a). Monodelphic, posterior extremity invaginated. Vulva situated at 74.2 [70.4–91.6 (81.7)], n = 6, from caudal extremity, vagina vera 34.1 [32.4–41.1 (37.5)] long, n = 6, vestibule 259.4 [219.6–258.1 (238.3)] long, n = 7, sphincter 50.6 [47.0–57.2 (51.6)] long and 50.7 [50.3–53.9 (52.0)] wide, n = 8, and infundibulum 118.7 [108.3–116.7 (112.1)] long, n = 6. Uterus 1.69 [1.56–1.78 (1.67)] mm long, n = 3. Number of eggs 16 [13–18 (16)], n = 6. Tail 29.6 [30.7–57.7 (45.3)] long, n = 7. Eggs 73.3 [71.3–89.1 (77.9)] long and 33.2 [30.5–43.4 (35.9)] wide, n = 6 (fig. 1k).
Taxonomic summary
Type host. Euryoryzomys russatus (Wagner, 1848) (Rodentia, Cricetidae, Sigmodontinae).
Type locality. Serra do Tabuleiro State Park (27°52′27″S, 48°49′26″W), municipality of Santo Amaro da Imperatriz, Santa Catarina state, Brazil.
Site of infection. Small intestine.
Prevalence. 25% (7 rodents infected / 28 rodents collected).
Mean intensity. 25.5 ± 16.9.
Mean abundance. 6.39 ± 13.8.
Type material. Holotype accession number CHIOC no. 38566a (male); allotype accession number CHIOC no. 38566b (female); paratypes’ accession number CHIOC no. 38566c (3 males and 3 females).
Etymology. The new species is named in honour of Antônio Rolando Oliveira de Castro.
Discussion
The presence of 24–27 ridges in the synlophe at the mid-body, unequal in size, the dissymmetrical caudal bursa and the prominent genital cone (Durette-Desset, Reference Durette-Desset1971; Durette-Desset & Digiani, Reference Durette-Desset and Digiani2012) permit the inclusion of the studied specimens in the genus Stilestrongylus (Heligmonellidae, Nippostrongylinae).
Among the 23 Neotropical species, S. aureus (Durette-Desset & Sutton, 1985) from Argentina, S. azarai (Durette-Desset & Sutton, 1985) from Argentina, S. flavescens (Sutton & Durette-Desset, 1991) from Uruguay, S. franciscanus (Digiani & Durette-Desset, 2002) from Argentina, S. gracielae (Digiani & Durette-Desset, 2006) from Argentina and S. oryzomysi (Sutton & Durette-Desset, 1991) from Argentina are closely related to S. rolandoi n. sp. The new species has caudal bursa patterns of types 1–4 and hypertrophy of the right lobe, and rays 4 and 5 are of equivalent length and divergent at the extremity. Although S. aureus presents caudal bursa pattern 1–4 in the right lobe, the left caudal bursa pattern is of type 2–3, tending to 2-2-1; S. azarai differs from S. rolandoi n. sp. by having right lobe with rays 4 and 6 divergent at their extremity, and S. oryzomysi by having right ray 4 smaller than right ray 5, and rays 4, 5 and 6 diverging at the same level; S. franciscanus is distinguished by rays 3 not reaching the edge of the caudal bursa and by the bifurcation of the dorsal ray at the middle of the trunk; S. flavescens is differentiated by its right rays 2 and 3 diverging at ‘V’; and S. gracielae is distinguished by its long rays 6 and very small spicules (100 μm). Stilestrongylus rolandoi n. sp. has the longest spicules in the genus (SpL/BL 21–33%), exceeding those of S. lanfrediae (SpL/BL 20%).
Panisse et al. (Reference Panisse, Robles, Digiani, Notarnicola, Galliari and Navone2017) reported the presence of a new species of Stilestrongylus infecting E. russatus and Sooretamys angouya from the Atlantic Forest in north-eastern Argentina. This species needs to be described in detail, and illustrations should be provided to clarify whether it constitutes the same species as that described here, as it was found in the same host species and in the same biogeographical region.
The main characteristics of the new species are the pattern of the caudal bursa, ray 2 of the left lobe being longer than ray 2 of the right lobe, the small rays 6, the asymmetry of rays 8, the high number of ridges (27 in males and 24 in females), and the longest spicule length to body length ratio in the genus. All these characteristics provide evidence that the nematodes from E. russatus are a new species of Stilestrongylus.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank T.S. Cardoso and S.F. Costa-Neto of Laboratório de Biologia e Parasitologia de Mamíferos Silvestres Reservatórios at FIOCRUZ for collection of rodents and helminths, R. Chmidt of the Platform of Image Production and Treatment at FIOCRUZ for help with the figure, Dr P.S. D'Andrea for the ICMBio licence, Dr P.C. Estrela for identification of rodents, and Drs R. Cerqueira and P.C. Estrela for coordination of the project PPBio Rede BioM.A (457524/2012-0).
Financial support
This Project was supported financially by Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico – CNPq – PPBio Rede BioM.A(457524/2012-0) and Instituto Oswaldo Cruz. RGMCB and BEAS received grants from Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior (CAPES), and ROS received grants from Fundação Carlos Chagas Filho de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado do Rio de Janeiro (FAPERJ).
Conflict of interest
None.
Ethical standards
Animals were captured under the authorization of the Brazilian Government's Chico Mendes Institute for Biodiversity and Conservation (ICMBIO, license number 26934-1) and the Environmental Foundation of Santa Catarina State (FATMA, license number 043/2014). All procedures followed the guidelines for capture, handling and care of animals of the Ethical Committee on Animal Use of the Oswaldo Cruz Foundation (CEUA license number LW – 39/14).