Crossref Citations
This article has been cited by the following publications. This list is generated based on data provided by
Crossref.
Grandemange, M.
Gohlke, M.
and
Cadot, O.
2013.
Bi-stability in the turbulent wake past parallelepiped bodies with various aspect ratios and wall effects.
Physics of Fluids,
Vol. 25,
Issue. 9,
Grandemange, M.
Mary, A.
Gohlke, M.
and
Cadot, O.
2013.
Effect on drag of the flow orientation at the base separation of a simplified blunt road vehicle.
Experiments in Fluids,
Vol. 54,
Issue. 5,
Krajnovic, Prof., Sinisa
Barros, D.
Ruiz, T.
Borée, J.
and
Noack, B.
2014.
Control of a three-dimensional blunt body wake using low and high frequency pulsed jets.
International Journal of Flow Control,
Vol. 6,
Issue. 1,
p.
61.
Parkin, Derwin J.
Thompson, M. C.
and
Sheridan, J.
2014.
Numerical analysis of bluff body wakes under periodic open-loop control.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 739,
Issue. ,
p.
94.
Kaiser, Eurika
Noack, Bernd R.
Cordier, Laurent
Spohn, Andreas
Segond, Marc
Abel, Markus
Daviller, Guillaume
Östh, Jan
Krajnović, Siniša
and
Niven, Robert K.
2014.
Cluster-based reduced-order modelling of a mixing layer.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 754,
Issue. ,
p.
365.
Grandemange, M.
Gohlke, M.
and
Cadot, O.
2014.
Turbulent wake past a three-dimensional blunt body. Part 2. Experimental sensitivity analysis.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 752,
Issue. ,
p.
439.
Östh, Jan
Noack, Bernd R.
Krajnović, Siniša
Barros, Diogo
and
Borée, Jacques
2014.
On the need for a nonlinear subscale turbulence term in POD models as exemplified for a high-Reynolds-number flow over an Ahmed body.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 747,
Issue. ,
p.
518.
Rigas, G.
Oxlade, A. R.
Morgans, A. S.
and
Morrison, J. F.
2014.
Low-dimensional dynamics of a turbulent axisymmetric wake.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 755,
Issue. ,
Yang, Jianzhi
Liu, Minghou
Wu, Guang
Zhong, Wei
and
Zhang, Xintai
2014.
Numerical study on coherent structure behind a circular disk.
Journal of Fluids and Structures,
Vol. 51,
Issue. ,
p.
172.
Grandemange, M.
Gohlke, M.
and
Cadot, O.
2014.
Statistical axisymmetry of the turbulent sphere wake.
Experiments in Fluids,
Vol. 55,
Issue. 11,
Yang, Jianzhi
Liu, Minghou
Wu, Guang
Liu, Quan
and
Zhang, Xintai
2015.
Low-frequency characteristics in the wake of a circular disk.
Physics of Fluids,
Vol. 27,
Issue. 6,
Volpe, Raffaele
Devinant, Philippe
and
Kourta, Azeddine
2015.
Experimental characterization of the unsteady natural wake of the full-scale square back Ahmed body: flow bi-stability and spectral analysis.
Experiments in Fluids,
Vol. 56,
Issue. 5,
Oxlade, Anthony R.
Morrison, Jonathan F.
Qubain, Ala
and
Rigas, Georgios
2015.
High-frequency forcing of a turbulent axisymmetric wake.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 770,
Issue. ,
p.
305.
Grandemange, M.
Cadot, O.
Courbois, A.
Herbert, V.
Ricot, D.
Ruiz, T.
and
Vigneron, R.
2015.
A study of wake effects on the drag of Ahmed׳s squareback model at the industrial scale.
Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics,
Vol. 145,
Issue. ,
p.
282.
Cadot, Olivier
Evrard, Antoine
and
Pastur, Luc
2015.
Imperfect supercritical bifurcation in a three-dimensional turbulent wake.
Physical Review E,
Vol. 91,
Issue. 6,
Ashok, A.
Van Buren, T.
and
Smits, A. J.
2015.
Asymmetries in the wake of a submarine model in pitch.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 774,
Issue. ,
p.
416.
Zhang, B. F.
Zhou, Y.
and
To, S.
2015.
Unsteady flow structures around a high-drag Ahmed body.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 777,
Issue. ,
p.
291.
Parkin, D.
Sheridan, J.
and
Thompson, M.C.
2015.
Numerical analysis of periodic open-loop flow control on bluff bodies in ground proximity.
Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics,
Vol. 145,
Issue. ,
p.
339.
Ashok, A.
Van Buren, T.
and
Smits, A. J.
2015.
The structure of the wake generated by a submarine model in yaw.
Experiments in Fluids,
Vol. 56,
Issue. 6,
Pasquetti, Richard
and
Peres, Noele
2015.
A penalty model of synthetic micro-jet actuator with application to the control of wake flows.
Computers & Fluids,
Vol. 114,
Issue. ,
p.
203.
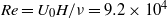 $\mathit{Re}= {U}_{0} H/ \nu = 9. 2\times 1{0}^{4} $ (where
$\mathit{Re}= {U}_{0} H/ \nu = 9. 2\times 1{0}^{4} $ (where 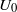 ${U}_{0} $ is free-stream velocity,
${U}_{0} $ is free-stream velocity, 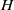 $H$ the height of the body and
$H$ the height of the body and  $\nu $ viscosity). The very large recirculation on the base responsible for the dominant part of the drag is characterized. The analyses of the coherent dynamics of the wake reveal the presence of two very distinctive time scales. At long time scales
$\nu $ viscosity). The very large recirculation on the base responsible for the dominant part of the drag is characterized. The analyses of the coherent dynamics of the wake reveal the presence of two very distinctive time scales. At long time scales 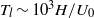 ${T}_{l} \sim 1{0}^{3} H/ {U}_{0} $, the recirculation region shifts between two preferred reflectional-symmetry-breaking positions leading to a statistically symmetric wake; the sequence of these asymmetric states is random. This bi-stable behaviour is independent of the Reynolds number but occurs only above a critical value of ground clearance. At short time scales
${T}_{l} \sim 1{0}^{3} H/ {U}_{0} $, the recirculation region shifts between two preferred reflectional-symmetry-breaking positions leading to a statistically symmetric wake; the sequence of these asymmetric states is random. This bi-stable behaviour is independent of the Reynolds number but occurs only above a critical value of ground clearance. At short time scales 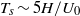 ${T}_{s} \sim 5H/ {U}_{0} $, the wake presents weak coherent oscillations in the vertical and lateral directions. They are respectively associated with the interaction of the top/bottom and lateral shear layers; when normalized by the height and width of the body, the Strouhal numbers are close to 0.17. These results suggest an alternate shedding associated with the vertical oscillation and a one-sided vortex shedding in the lateral direction with an orientation linked to the current asymmetric position. Finally, the impact of these coherent wake motions on the base pressure is discussed to motivate further drag reduction strategies.
${T}_{s} \sim 5H/ {U}_{0} $, the wake presents weak coherent oscillations in the vertical and lateral directions. They are respectively associated with the interaction of the top/bottom and lateral shear layers; when normalized by the height and width of the body, the Strouhal numbers are close to 0.17. These results suggest an alternate shedding associated with the vertical oscillation and a one-sided vortex shedding in the lateral direction with an orientation linked to the current asymmetric position. Finally, the impact of these coherent wake motions on the base pressure is discussed to motivate further drag reduction strategies.