Crossref Citations
This article has been cited by the following publications. This list is generated based on data provided by
Crossref.
Lelouvetel, J.
Tanaka, T.
Sato, Y.
and
Hishida, K.
2014.
Transport mechanisms of the turbulent energy cascade in upward/downward bubbly flows.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 741,
Issue. ,
p.
514.
Hazuku, Tatsuya
Takamasa, Tomoji
and
Hibiki, Takashi
2015.
Phase Distribution Characteristics of Bubbly Flow in Mini Pipes Under Normal and Microgravity Conditions.
Microgravity Science and Technology,
Vol. 27,
Issue. 2,
p.
75.
Konishi, Christopher
and
Mudawar, Issam
2015.
Review of flow boiling and critical heat flux in microgravity.
International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer,
Vol. 80,
Issue. ,
p.
469.
Kharangate, Chirag R.
O’Neill, Lucas E.
and
Mudawar, Issam
2016.
Effects of two-phase inlet quality, mass velocity, flow orientation, and heating perimeter on flow boiling in a rectangular channel: Part 1 – Two-phase flow and heat transfer results.
International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer,
Vol. 103,
Issue. ,
p.
1261.
Li, Guohui
and
Li, Xiangli
2016.
Effects of Reduced Gravity Conditions on Bubble Dispersion Characteristics in the Bubble Column.
Microgravity Science and Technology,
Vol. 28,
Issue. 4,
p.
441.
Kriebitzsch, Sebastian
and
Rzehak, Roland
2016.
Baseline Model for Bubbly Flows: Simulation of Monodisperse Flow in Pipes of Different Diameters.
Fluids,
Vol. 1,
Issue. 3,
p.
29.
Chahed, Jamel
Aouadi, Aroua
Rezig, Mariem
and
Bellakhal, Ghazi
2016.
The Phenomenon of Bubbles Negative Relative Velocity in Vertical Bubbly Jets.
Journal of Fluids Engineering,
Vol. 138,
Issue. 12,
Mudawar, Issam
2017.
Vol. 49,
Issue. ,
p.
225.
Rezig, Mariem
Bellakhal, Ghazi
and
Chahed, Jamel
2017.
Phase distribution in dispersed liquid–liquid flow in vertical pipe: Mean and turbulent contributions of interfacial force.
AIChE Journal,
Vol. 63,
Issue. 9,
p.
4214.
Chahed, Jamel
Bellakhel, Ghazi
and
Kanfoudi, Hatem
2017.
Bubbles’ slip velocity reduction in the near wall region of turbulent bubbly pipe flows under different gravity conditions.
Chemical Engineering Research and Design,
Vol. 119,
Issue. ,
p.
231.
Krejčí, Jan
Ježová, Lucie
Kučerová, Radka
Plička, Robert
Broža, Štěpán
Krejčí, David
and
Ventrubová, Iva
2017.
The measurement of small flow.
Sensors and Actuators A: Physical,
Vol. 266,
Issue. ,
p.
308.
Ayeb Mrabtini, Hela
Bellakhal, Ghazi
and
Chahed, Jamel
2017.
Analysis of the homogeneous turbulence structure in uniformly sheared bubbly flow.
Nuclear Engineering and Design,
Vol. 320,
Issue. ,
p.
112.
Bakhuis, Dennis
Verschoof, Ruben A.
Mathai, Varghese
Huisman, Sander G.
Lohse, Detlef
and
Sun, Chao
2018.
Finite-sized rigid spheres in turbulent Taylor–Couette flow: effect on the overall drag.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 850,
Issue. ,
p.
246.
Aouadi, Aroua
Bellakhal, Ghazi
and
Chahed, Jamel
2019.
Effect of the turbulent contribution of the interfacial momentum transfer on the bubbles dynamics and void fraction distribution in vertical bubbly jets.
International Journal of Multiphase Flow,
Vol. 114,
Issue. ,
p.
82.
du Cluzeau, A.
Bois, G.
and
Toutant, A.
2019.
Analysis and modelling of Reynolds stresses in turbulent bubbly up-flows from direct numerical simulations.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 866,
Issue. ,
p.
132.
Bellakhal, Ghazi
Chaibina, Fathia
and
Chahed, Jamel
2020.
Assessment of turbulence models for bubbly flows: Toward a five-equation turbulence model.
Chemical Engineering Science,
Vol. 220,
Issue. ,
p.
115425.
Iceri, Daiane Mieko
Zummo, Giuseppe
Saraceno, Luca
and
Ribatski, Gherhardt
2020.
Convective boiling heat transfer under microgravity and hypergravity conditions.
International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer,
Vol. 153,
Issue. ,
p.
119614.
Chahed, Jamel
and
Masbernat, Lucien
2020.
Modeling Interfacial Interactions and Turbulence in the Near-Wall Region of a Vertical Bubbly Boundary Layer.
Journal of Fluids Engineering,
Vol. 142,
Issue. 6,
Sitompul, Yos Panagaman
Aoki, Takayuki
and
Takaki, Tomohiro
2021.
Simulation of turbulent bubbly pipe flow with high density ratio and high reynolds number by using the lattice boltzmann method and a multi-phase field model.
International Journal of Multiphase Flow,
Vol. 134,
Issue. ,
p.
103505.
Islam, Tarikul
and
Rehman, Mahfoozur
2021.
A Sensitive Fiber Optic Technique for Remote Measurement of Liquid Flow.
p.
12.
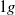 ,
, 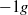 and
and 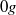 ), have been performed to understand the influence of gravity upon the flow structure and the phase distribution. The mean and fluctuating phase velocities, shear stress, turbulence production, gas fraction and bubble size have been measured or determined. The results for
), have been performed to understand the influence of gravity upon the flow structure and the phase distribution. The mean and fluctuating phase velocities, shear stress, turbulence production, gas fraction and bubble size have been measured or determined. The results for 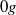 flow obtained during parabolic flights are taken as reference for buoyant
flow obtained during parabolic flights are taken as reference for buoyant 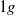 and
and 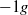 flows. Three buoyancy numbers are introduced to understand and quantify the effects of gravity with respect to friction. We show that the kinematic structure of the liquid is similar to single-phase flow for
flows. Three buoyancy numbers are introduced to understand and quantify the effects of gravity with respect to friction. We show that the kinematic structure of the liquid is similar to single-phase flow for 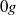 flow whereas it deviates in
flow whereas it deviates in 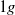 and
and 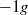 buoyant flows. The present results confirm the existence of a two-layer structure for buoyant flows with a nearly homogeneous core and a wall layer similar to the single-phase inertial layer whose thickness seems to result from a friction–gravity balance. The distributions of phase velocity, shear stress and turbulence are discussed in the light of various existing physical models. This leads to a dimensionless correlation that quantifies the wall shear stress increase due to buoyancy. The turbulent dispersion, the lift and the nonlinear effects of added mass are taken into account in a simplified model for the phase distribution. Its analytical solution gives a qualitative description of the gas fraction distribution in the wall layer.
buoyant flows. The present results confirm the existence of a two-layer structure for buoyant flows with a nearly homogeneous core and a wall layer similar to the single-phase inertial layer whose thickness seems to result from a friction–gravity balance. The distributions of phase velocity, shear stress and turbulence are discussed in the light of various existing physical models. This leads to a dimensionless correlation that quantifies the wall shear stress increase due to buoyancy. The turbulent dispersion, the lift and the nonlinear effects of added mass are taken into account in a simplified model for the phase distribution. Its analytical solution gives a qualitative description of the gas fraction distribution in the wall layer.

