Published online by Cambridge University Press: 08 February 2013
Vortices in stably stratified fluids generally have a pancake shape with a small vertical thickness compared with their horizontal size. In order to understand what mechanism determines their minimum thickness, the linear stability of an axisymmetric pancake vortex is investigated as a function of its aspect ratio  $\alpha $, the horizontal Froude number
$\alpha $, the horizontal Froude number 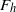 ${F}_{h} $, the Reynolds number
${F}_{h} $, the Reynolds number 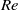 $\mathit{Re}$ and the Schmidt number
$\mathit{Re}$ and the Schmidt number 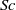 $\mathit{Sc}$. The vertical vorticity profile of the base state is chosen to be Gaussian in both radial and vertical directions. The vortex is unstable when the aspect ratio is below a critical value, which scales with the Froude number:
$\mathit{Sc}$. The vertical vorticity profile of the base state is chosen to be Gaussian in both radial and vertical directions. The vortex is unstable when the aspect ratio is below a critical value, which scales with the Froude number: 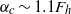 ${\alpha }_{c} \sim 1. 1{F}_{h} $ for sufficiently large Reynolds numbers. The most unstable perturbation has an azimuthal wavenumber either
${\alpha }_{c} \sim 1. 1{F}_{h} $ for sufficiently large Reynolds numbers. The most unstable perturbation has an azimuthal wavenumber either 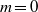 $m= 0$,
$m= 0$, 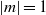 $\vert m\vert = 1$ or
$\vert m\vert = 1$ or 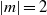 $\vert m\vert = 2$ depending on the control parameters. We show that the threshold corresponds to the appearance of gravitationally unstable regions in the vortex core due to the thermal wind balance. The Richardson criterion for shear instability based on the vertical shear is never satisfied alone. The dominance of the gravitational instability over the shear instability is shown to hold for a general class of pancake vortices with angular velocity of the form
$\vert m\vert = 2$ depending on the control parameters. We show that the threshold corresponds to the appearance of gravitationally unstable regions in the vortex core due to the thermal wind balance. The Richardson criterion for shear instability based on the vertical shear is never satisfied alone. The dominance of the gravitational instability over the shear instability is shown to hold for a general class of pancake vortices with angular velocity of the form 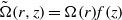 $\tilde {\Omega } (r, z)= \Omega (r)f(z)$ provided that
$\tilde {\Omega } (r, z)= \Omega (r)f(z)$ provided that 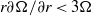 $r\partial \Omega / \partial r\lt 3\Omega $ everywhere. Finally, the growth rate and azimuthal wavenumber selection of the gravitational instability are accounted well by considering an unstably stratified viscous and diffusive layer in solid body rotation with a parabolic density gradient.
$r\partial \Omega / \partial r\lt 3\Omega $ everywhere. Finally, the growth rate and azimuthal wavenumber selection of the gravitational instability are accounted well by considering an unstably stratified viscous and diffusive layer in solid body rotation with a parabolic density gradient.