Crossref Citations
This article has been cited by the following publications. This list is generated based on data provided by
Crossref.
MacTaggart, D.
2018.
The non-modal onset of the tearing instability.
Journal of Plasma Physics,
Vol. 84,
Issue. 5,
Herreman, W.
2018.
Minimal perturbation flows that trigger mean field dynamos in shear flows.
Journal of Plasma Physics,
Vol. 84,
Issue. 3,
Li, Kuan
Jackson, Andrew
and
Livermore, Philip W.
2018.
Taylor state dynamos found by optimal control: axisymmetric examples.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 853,
Issue. ,
p.
647.
Holdenried-Chernoff, D.
Chen, L.
and
Jackson, A.
2019.
A trio of simple optimized axisymmetric kinematic dynamos in a sphere.
Proceedings of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences,
Vol. 475,
Issue. 2229,
p.
20190308.
Metman, Maurits C
Livermore, Philip W
Mound, Jonathan E
and
Beggan, Ciarán D
2019.
Modelling decadal secular variation with only magnetic diffusion.
Geophysical Journal International,
Vol. 219,
Issue. Supplement_1,
p.
S58.
Luo, Jiawen
Chen, Long
Li, Kuan
and
Jackson, Andrew
2020.
Optimal kinematic dynamos in a sphere.
Proceedings of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences,
Vol. 476,
Issue. 2233,
p.
20190675.
Vidal, Jérémie
and
Cébron, David
2020.
Acoustic and inertial modes in planetary-like rotating ellipsoids.
Proceedings of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences,
Vol. 476,
Issue. 2239,
p.
20200131.
Metman, Maurits C.
Beggan, Ciarán D.
Livermore, Philip W.
and
Mound, Jonathan E.
2020.
Forecasting yearly geomagnetic variation through sequential estimation of core flow and magnetic diffusion.
Earth, Planets and Space,
Vol. 72,
Issue. 1,
Brandenburg, Axel
and
Chen, Long
2020.
The nature of mean-field generation in three classes of optimal dynamos.
Journal of Plasma Physics,
Vol. 86,
Issue. 1,
Marti, Philippe
and
Jackson, Andrew
2021.
Accurate and efficient Jones-Worland spectral transforms for planetary applications.
p.
1.
Fouxon, Itzhak
Feinberg, Joshua
and
Mond, Michael
2021.
Linear and nonlinear hydromagnetic stability in laminar and turbulent flows.
Physical Review E,
Vol. 103,
Issue. 4,
Gerick, F.
Jault, D.
and
Noir, J.
2021.
Fast Quasi‐Geostrophic Magneto‐Coriolis Modes in the Earth's Core.
Geophysical Research Letters,
Vol. 48,
Issue. 4,
Vidal, Jérémie
and
Cébron, David
2021.
Kinematic dynamos in triaxial ellipsoids.
Proceedings of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences,
Vol. 477,
Issue. 2252,
Landeau, Maylis
Fournier, Alexandre
Nataf, Henri-Claude
Cébron, David
and
Schaeffer, Nathanaël
2022.
Sustaining Earth’s magnetic dynamo.
Nature Reviews Earth & Environment,
Vol. 3,
Issue. 4,
p.
255.
Bachtiar, A. A.
and
James, R. W.
2022.
Dynamos driven by modified Beltrami flows, and a search for related planar flow dynamos.
Geophysical & Astrophysical Fluid Dynamics,
Vol. 116,
Issue. 2,
p.
140.
Chen, Long
2022.
Multiplicity in an optimised kinematic dynamo.
Geophysical & Astrophysical Fluid Dynamics,
Vol. 116,
Issue. 4,
p.
290.
Vidal, Jérémie
and
Cébron, David
2023.
Precession-driven flows in stress-free ellipsoids.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 954,
Issue. ,
Shebalin, John V.
2024.
The Statistical Mechanics of Ideal Magnetohydrodynamic Turbulence and a Solution of the Dynamo Problem.
Fluids,
Vol. 9,
Issue. 2,
p.
46.
Lherm, Victor
Nakajima, Miki
and
Blackman, Eric G.
2024.
Thermal and magnetic evolution of an Earth-like planet with a basal magma ocean.
Physics of the Earth and Planetary Interiors,
Vol. 356,
Issue. ,
p.
107267.
Gerick, F.
and
Livermore, P. W.
2024.
Interannual Magneto–Coriolis modes and their sensitivity on the magnetic field within the Earth’s core.
Proceedings of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences,
Vol. 480,
Issue. 2299,
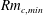 $Rm_{c,min}$ for the onset of a dynamo. Although nonlinear, this iteration procedure converges to a single solution and there is no evidence that this is not a global optimum. We find that
$Rm_{c,min}$ for the onset of a dynamo. Although nonlinear, this iteration procedure converges to a single solution and there is no evidence that this is not a global optimum. We find that 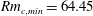 $Rm_{c,min}=64.45$ is at least three times lower than that of any published example of a spherical kinematic dynamo generated by steady flows, and our optimal dynamo clearly operates above the theoretical lower bounds for dynamo action. The corresponding optimal flow has a spatially localized helical structure in the centre of the sphere, and the dominant components are invariant under rotation by
$Rm_{c,min}=64.45$ is at least three times lower than that of any published example of a spherical kinematic dynamo generated by steady flows, and our optimal dynamo clearly operates above the theoretical lower bounds for dynamo action. The corresponding optimal flow has a spatially localized helical structure in the centre of the sphere, and the dominant components are invariant under rotation by  $\unicode[STIX]{x03C0}$.
$\unicode[STIX]{x03C0}$.

