Crossref Citations
This article has been cited by the following publications. This list is generated based on data provided by
Crossref.
Favier, B.
and
Proctor, M. R. E.
2013.
Kinematic dynamo action in square and hexagonal patterns.
Physical Review E,
Vol. 88,
Issue. 5,
Tilgner, A.
2014.
Magnetic energy dissipation and mean magnetic field generation in planar convection-driven dynamos.
Physical Review E,
Vol. 90,
Issue. 1,
Ivers, D. J.
and
Phillips, C. G.
2014.
Homogeneous planar and two-dimensional mean-field antidynamo theorems with zero mean flow.
Geophysical & Astrophysical Fluid Dynamics,
Vol. 108,
Issue. 6,
p.
716.
Masada, Youhei
and
Sano, Takayoshi
2014.
MEAN-FIELD MODELING OF AN α
2
DYNAMO COUPLED WITH DIRECT NUMERICAL SIMULATIONS OF RIGIDLY ROTATING CONVECTION
.
The Astrophysical Journal,
Vol. 794,
Issue. 1,
p.
L6.
Masada, Youhei
and
Sano, Takayoshi
2014.
Long-term evolution of large-scale magnetic fields in rotating stratified convection.
Publications of the Astronomical Society of Japan,
Vol. 66,
Issue. SP1,
Favier, B.
Silvers, L. J.
and
Proctor, M. R. E.
2014.
Inverse cascade and symmetry breaking in rapidly rotating Boussinesq convection.
Physics of Fluids,
Vol. 26,
Issue. 9,
Guervilly, Céline
Hughes, David W.
and
Jones, Chris A.
2015.
Generation of magnetic fields by large-scale vortices in rotating convection.
Physical Review E,
Vol. 91,
Issue. 4,
Witzke, V.
Silvers, L. J.
and
Favier, B.
2016.
Evolution of forced shear flows in polytropic atmospheres: a comparison of forcing methods and energetics.
Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society,
Vol. 463,
Issue. 1,
p.
282.
Brun, Allan Sacha
and
Browning, Matthew K.
2017.
Magnetism, dynamo action and the solar-stellar connection.
Living Reviews in Solar Physics,
Vol. 14,
Issue. 1,
Bushby, P. J.
Käpylä, P. J.
Masada, Y.
Brandenburg, A.
Favier, B.
Guervilly, C.
and
Käpylä, M. J.
2018.
Large-scale dynamos in rapidly rotating plane layer convection.
Astronomy & Astrophysics,
Vol. 612,
Issue. ,
p.
A97.
Ivers, D.J.
and
Phillips, C.G.
2018.
Effects of anisotropic turbulent thermal diffusion on spherical magnetoconvection in the Earth’s core.
Physics of the Earth and Planetary Interiors,
Vol. 276,
Issue. ,
p.
44.
Makarenko, I.
Bushby, P.
Fletcher, A.
Henderson, R.
Makarenko, N.
and
Shukurov, A.
2018.
Topological data analysis and diagnostics of compressible magnetohydrodynamic turbulence.
Journal of Plasma Physics,
Vol. 84,
Issue. 4,
Witzke, V
Silvers, L J
and
Favier, B
2019.
Evolution and characteristics of forced shear flows in polytropic atmospheres: large and small Péclet number regimes.
Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society,
Vol. 482,
Issue. 1,
p.
1338.
Evirgen, C C
Gent, F A
Shukurov, A
Fletcher, A
and
Bushby, P J
2019.
The supernova-regulated ISM – VI. Magnetic effects on the structure of the interstellar medium.
Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society,
Vol. 488,
Issue. 4,
p.
5065.
Cooper, R. G.
Bushby, P. J.
and
Guervilly, C.
2020.
Subcritical dynamos in rapidly rotating planar convection.
Physical Review Fluids,
Vol. 5,
Issue. 11,
Yushkov, E. V.
Allahverdiyev, R.
and
Sokoloff, D. D.
2020.
Mean-Field Dynamo Model in Anisotropic Uniform Turbulent Flow with Short-Time Correlations.
Galaxies,
Vol. 8,
Issue. 3,
p.
68.
Yan, Ming
and
Calkins, Michael A.
2022.
Asymptotic behaviour of rotating convection-driven dynamos in the plane layer geometry.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 951,
Issue. ,
Yan, Ming
and
Calkins, Michael A.
2022.
Strong large scale magnetic fields in rotating convection-driven dynamos: The important role of magnetic diffusion.
Physical Review Research,
Vol. 4,
Issue. 1,
Naskar, Souvik
and
Pal, Anikesh
2022.
Direct numerical simulations of optimal thermal convection in rotating plane layer dynamos.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 942,
Issue. ,
Duguid, Craig D
Bushby, Paul J
and
Wood, Toby S
2023.
Shear-driven magnetic buoyancy in the solar tachocline: the mean electromotive force due to rotation.
Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society,
Vol. 520,
Issue. 1,
p.
527.
 $\alpha $-effect, which is one of the key ingredients in any mean-field dynamo model. Provided that this
$\alpha $-effect, which is one of the key ingredients in any mean-field dynamo model. Provided that this  $\alpha $-effect operates more efficiently than (turbulent) magnetic diffusion, such a system should be capable of sustaining a large-scale dynamo. However, in the Boussinesq model that was considered by Cattaneo & Hughes (J. Fluid Mech., vol. 553, 2006, pp. 401–418) the dynamo produced small-scale, intermittent magnetic fields with no significant large-scale component. In this paper, we consider the compressible analogue of the rotating convective layer that was considered by Cattaneo & Hughes (2006). Varying the horizontal scale of the computational domain, we investigate the dependence of the dynamo upon the rotation rate. Our simulations indicate that these turbulent compressible flows can drive a small-scale dynamo but, even when the layer is rotating very rapidly (with a mid-layer Taylor number of
$\alpha $-effect operates more efficiently than (turbulent) magnetic diffusion, such a system should be capable of sustaining a large-scale dynamo. However, in the Boussinesq model that was considered by Cattaneo & Hughes (J. Fluid Mech., vol. 553, 2006, pp. 401–418) the dynamo produced small-scale, intermittent magnetic fields with no significant large-scale component. In this paper, we consider the compressible analogue of the rotating convective layer that was considered by Cattaneo & Hughes (2006). Varying the horizontal scale of the computational domain, we investigate the dependence of the dynamo upon the rotation rate. Our simulations indicate that these turbulent compressible flows can drive a small-scale dynamo but, even when the layer is rotating very rapidly (with a mid-layer Taylor number of 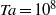 $Ta= 1{0}^{8} $), we find no evidence for the generation of a significant large-scale component of the magnetic field on a dynamical time scale. Like Cattaneo & Hughes (2006), we measure a negligible (time-averaged)
$Ta= 1{0}^{8} $), we find no evidence for the generation of a significant large-scale component of the magnetic field on a dynamical time scale. Like Cattaneo & Hughes (2006), we measure a negligible (time-averaged)  $\alpha $-effect when a uniform horizontal magnetic field is imposed across the computational domain. Although the total horizontal magnetic flux is a conserved quantity in these simulations, the (depth-dependent) horizontally averaged magnetic field always exhibits strong fluctuations. If these fluctuations are artificially suppressed within the code, we measure a significant mean electromotive force that is comparable to that found in related calculations in which the
$\alpha $-effect when a uniform horizontal magnetic field is imposed across the computational domain. Although the total horizontal magnetic flux is a conserved quantity in these simulations, the (depth-dependent) horizontally averaged magnetic field always exhibits strong fluctuations. If these fluctuations are artificially suppressed within the code, we measure a significant mean electromotive force that is comparable to that found in related calculations in which the  $\alpha $-effect is measured using the test-field method, even though we observe no large-scale dynamo action.
$\alpha $-effect is measured using the test-field method, even though we observe no large-scale dynamo action.