Article contents
On grid-generated turbulence in the near- and far field regions
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 24 July 2014
Abstract
Using a conventional bi-planar turbulence-generating grid, we confirm the recent findings (Valente & Vassilicos, Phys. Rev. Lett., vol. 108, 2012, art. 214503) that show there is a turbulence decay region close to the generating grid that departs from the ‘classical’ turbulence decay (Comte-Bellot & Corrsin, J. Fluid Mech., vol. 25, 1966, pp. 657–682). In this ‘near-field’ region, the turbulence energy decays more rapidly than in the far-field and it exhibits unusual scaling properties. Based on the velocity decay laws, we show that for our conventional grid, the near-field extends from 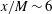 $\def \xmlpi #1{}\def \mathsfbi #1{\boldsymbol {\mathsf {#1}}}\let \le =\leqslant \let \leq =\leqslant \let \ge =\geqslant \let \geq =\geqslant \def \Pr {\mathit {Pr}}\def \Fr {\mathit {Fr}}\def \Rey {\mathit {Re}}x/M \sim 6$ to
$\def \xmlpi #1{}\def \mathsfbi #1{\boldsymbol {\mathsf {#1}}}\let \le =\leqslant \let \leq =\leqslant \let \ge =\geqslant \let \geq =\geqslant \def \Pr {\mathit {Pr}}\def \Fr {\mathit {Fr}}\def \Rey {\mathit {Re}}x/M \sim 6$ to 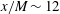 $x/M \sim 12$ where
$x/M \sim 12$ where  $x$ is the downstream distance from the grid and
$x$ is the downstream distance from the grid and 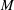 $M$ is the mesh size. This corresponds to
$M$ is the mesh size. This corresponds to 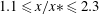 $1.1 \le x/x* \le 2.3$ where
$1.1 \le x/x* \le 2.3$ where 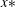 $x*$ is the wake interaction length scale (Mazellier & Vassilicos, Phys. Fluids, vol. 22, 2010, art. 075101). However, other statistics (velocity derivatives and length-scale ratios) indicate that the extent of the initial period depends on the grid mesh Reynolds number,
$x*$ is the wake interaction length scale (Mazellier & Vassilicos, Phys. Fluids, vol. 22, 2010, art. 075101). However, other statistics (velocity derivatives and length-scale ratios) indicate that the extent of the initial period depends on the grid mesh Reynolds number, 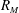 $R_M$, extending further for higher values of
$R_M$, extending further for higher values of 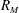 $R_M$. In the near-field the turbulence approaches isotropy both at the large and small scales but there still is inhomogeneity in the derivative statistics. The derivative skewness also departs from values observed at comparable Reynolds numbers in the far-field decay region, and in other turbulent flows at comparable Reynolds numbers. Two values of
$R_M$. In the near-field the turbulence approaches isotropy both at the large and small scales but there still is inhomogeneity in the derivative statistics. The derivative skewness also departs from values observed at comparable Reynolds numbers in the far-field decay region, and in other turbulent flows at comparable Reynolds numbers. Two values of 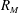 $R_M$ were studied:
$R_M$ were studied: 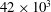 $42 \times 10^3$ and
$42 \times 10^3$ and 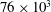 $76 \times 10^3$.
$76 \times 10^3$.
JFM classification
- Type
- Papers
- Information
- Copyright
- © 2014 Cambridge University Press
References
- 93
- Cited by


