Crossref Citations
This article has been cited by the following publications. This list is generated based on data provided by
Crossref.
Mezher, R
Abisset-Chavanne, E
Férec, J
Ausias, G
and
Chinesta, F
2015.
Direct simulation of concentrated fiber suspensions subjected to bending effects.
Modelling and Simulation in Materials Science and Engineering,
Vol. 23,
Issue. 5,
p.
055007.
Bounoua, S.
Lemaire, E.
Férec, J.
Ausias, G.
and
Kuzhir, P.
2016.
Shear-thinning in concentrated rigid fiber suspensions: Aggregation induced by adhesive interactions.
Journal of Rheology,
Vol. 60,
Issue. 6,
p.
1279.
Bounoua, Sihem
Kuzhir, Pavel
and
Lemaire, Elisabeth
2016.
Normal stress differences in non-Brownian fiber suspensions.
Journal of Rheology,
Vol. 60,
Issue. 4,
p.
661.
Tapia, Franco
Shaikh, Saif
Butler, Jason E.
Pouliquen, Olivier
and
Guazzelli, Élisabeth
2017.
Rheology of concentrated suspensions of non-colloidal rigid fibres.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 827,
Issue. ,
Nagy, Dániel B.
Claudin, Philippe
Börzsönyi, Tamás
and
Somfai, Ellák
2017.
Rheology of dense granular flows for elongated particles.
Physical Review E,
Vol. 96,
Issue. 6,
Leahy, Brian D.
Koch, Donald L.
and
Cohen, Itai
2017.
Controlling the alignment of rodlike colloidal particles with time-dependent shear flows.
Journal of Rheology,
Vol. 61,
Issue. 5,
p.
979.
Butler, Jason E.
2017.
Collective Dynamics of Particles.
Vol. 576,
Issue. ,
p.
99.
Osiptsov, Andrei A.
2017.
Fluid Mechanics of Hydraulic Fracturing: a Review.
Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering,
Vol. 156,
Issue. ,
p.
513.
Guazzelli, Élisabeth
Radjai, F.
Nezamabadi, S.
Luding, S.
and
Delenne, J.Y.
2017.
Rheology of dense suspensions of non colloidal particles.
EPJ Web of Conferences,
Vol. 140,
Issue. ,
p.
01001.
Foster, Peter J
Yan, Wen
Fürthauer, Sebastian
Shelley, Michael J
and
Needleman, Daniel J
2017.
Connecting macroscopic dynamics with microscopic properties in active microtubule network contraction.
New Journal of Physics,
Vol. 19,
Issue. 12,
p.
125011.
Uspal, W E
Popescu, M N
Tasinkevych, M
and
Dietrich, S
2018.
Shape-dependent guidance of active Janus particles by chemically patterned surfaces.
New Journal of Physics,
Vol. 20,
Issue. 1,
p.
015013.
Guazzelli, Élisabeth
and
Pouliquen, Olivier
2018.
Rheology of dense granular suspensions.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 852,
Issue. ,
Jenny, M.
Ferrari, M.
Gaudel, N.
and
de Richter, S. Kiesgen
2018.
Rheology of fiber suspensions using MRI.
EPL (Europhysics Letters),
Vol. 121,
Issue. 3,
p.
34003.
Butler, Jason E.
and
Snook, Braden
2018.
Microstructural Dynamics and Rheology of Suspensions of Rigid Fibers.
Annual Review of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 50,
Issue. 1,
p.
299.
Strednak, Scott
Shaikh, Saif
Butler, Jason E.
and
Guazzelli, Élisabeth
2018.
Shear-induced migration and orientation of rigid fibers in an oscillatory pipe flow.
Physical Review Fluids,
Vol. 3,
Issue. 9,
Mahajan, Vinay V.
Mehmood, Junaid
El Hasadi, Yousef M.F.
and
Padding, Johan T.
2019.
Fluid medium effect on stresses in suspensions of high-inertia rod-like particles.
Chemical Engineering Science: X,
Vol. 3,
Issue. ,
p.
100030.
Yan, Wen
Zhang, Huan
and
Shelley, Michael J.
2019.
Computing collision stress in assemblies of active spherocylinders: Applications of a fast and generic geometric method.
The Journal of Chemical Physics,
Vol. 150,
Issue. 6,
Mari, Romain
2020.
Shear thickening of suspensions of dimeric particles.
Journal of Rheology,
Vol. 64,
Issue. 2,
p.
239.
Bretonnet, Jean-Louis
and
Wax, Jean-François
2021.
Applicability conditions of the Stokes formula.
AIMS Materials Science,
Vol. 8,
Issue. 5,
p.
809.
Maklad, O.
and
Poole, R.J.
2021.
A review of the second normal-stress difference; its importance in various flows, measurement techniques, results for various complex fluids and theoretical predictions.
Journal of Non-Newtonian Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 292,
Issue. ,
p.
104522.
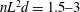 $\def \xmlpi #1{}\def \mathsfbi #1{\boldsymbol {\mathsf {#1}}}\let \le =\leqslant \let \leq =\leqslant \let \ge =\geqslant \let \geq =\geqslant \def \Pr {\mathit {Pr}}\def \Fr {\mathit {Fr}}\def \Rey {\mathit {Re}}nL^2d=1.5\text {--}3$ and aspect ratios of
$\def \xmlpi #1{}\def \mathsfbi #1{\boldsymbol {\mathsf {#1}}}\let \le =\leqslant \let \leq =\leqslant \let \ge =\geqslant \let \geq =\geqslant \def \Pr {\mathit {Pr}}\def \Fr {\mathit {Fr}}\def \Rey {\mathit {Re}}nL^2d=1.5\text {--}3$ and aspect ratios of 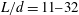 $L/d=11\text {--}32$, where
$L/d=11\text {--}32$, where  $n$ is the number of fibres per unit volume,
$n$ is the number of fibres per unit volume, 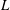 $L$ is the fibre length and
$L$ is the fibre length and 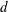 $d$ is the diameter. The first and second normal stress differences are determined experimentally from measuring the deformation in the free surface in a tilted trough and in a Weissenberg rheometer. Simulations are performed as well, and the hydrodynamic and contact contributions to the normal stresses are calculated. The experiments and simulations indicate that the second normal stress difference is negative and that its magnitude increases as the concentration is raised and the aspect ratio is lowered. The first normal stress difference is positive and its magnitude is approximately twice that of the second normal stress difference. Simulation results indicate that, for the concentrations and aspect ratios studied, contact forces between fibres form the dominant contribution to the normal stress differences.
$d$ is the diameter. The first and second normal stress differences are determined experimentally from measuring the deformation in the free surface in a tilted trough and in a Weissenberg rheometer. Simulations are performed as well, and the hydrodynamic and contact contributions to the normal stresses are calculated. The experiments and simulations indicate that the second normal stress difference is negative and that its magnitude increases as the concentration is raised and the aspect ratio is lowered. The first normal stress difference is positive and its magnitude is approximately twice that of the second normal stress difference. Simulation results indicate that, for the concentrations and aspect ratios studied, contact forces between fibres form the dominant contribution to the normal stress differences.

