No CrossRef data available.
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 13 December 2024
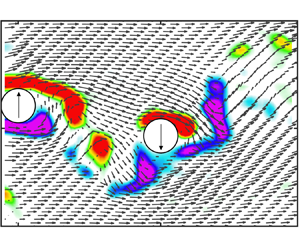
This study conducts experimental investigations into wake-induced vibration (WIV) of a circular cylinder placed downstream of an oscillating cylinder. Surprisingly, it is observed that the previously identified WIV phenomenon, characterized by a sustained increase in amplitude at higher reduced velocities, does not occur when the upstream cylinder oscillates at large amplitudes. Instead, a different phenomenon, which we refer to as the ‘wake-captured vibration’, becomes dominant. The experiments reveal a negative correlation between the vortex-induced vibration amplitude response of the upstream cylinder and the WIV amplitude response of the downstream cylinder. Through a quasi-steady and linear instability analysis, the study demonstrates that the previously proposed wake-displacement mechanism may not be applicable for predicting the cylinder WIV response in the wake of an oscillating body. This is because the lift force gradients across the wake, measured through stationary cylinder experiments, decrease significantly when the upstream cylinder vibrates at higher amplitudes. Consequently, actively controlled vibration experiments are conducted to systematically map the hydrodynamic properties of the downstream cylinder vibrating in the wake of an oscillating cylinder. The findings align with observations from free-vibration experiments, and help to explain the amplitude and frequency response of WIV. Additionally, wake visualization through particle image velocimetry is conducted to provide further insights into the complex wake and vortex–body interactions.