Crossref Citations
This article has been cited by the following publications. This list is generated based on data provided by
Crossref.
Hayashi, Kosuke
Hessenkemper, Hendrik
Lucas, Dirk
Legendre, Dominique
and
Tomiyama, Akio
2021.
Scaling of Lift Reversal of Deformed Bubbles in Air-Water Systems.
International Journal of Multiphase Flow,
Vol. 142,
Issue. ,
p.
103653.
Tas-Koehler, Sibel
Liao, Yixiang
and
Hampel, Uwe
2021.
A critical analysis of drag force modelling for disperse gas-liquid flow in a pipe with an obstacle.
Chemical Engineering Science,
Vol. 246,
Issue. ,
p.
117007.
Masuk, Ashik Ullah Mohammad
Qi, Yinghe
Salibindla, Ashwanth K.R.
and
Ni, Rui
2021.
Towards a phenomenological model on the deformation and orientation dynamics of finite-sized bubbles in both quiescent and turbulent media.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 920,
Issue. ,
Masuk, Ashik Ullah Mohammad
Salibindla, Ashwanth K. R.
and
Ni, Rui
2021.
Simultaneous measurements of deforming Hinze-scale bubbles with surrounding turbulence.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 910,
Issue. ,
Salibindla, Ashwanth K.R.
Masuk, Ashik Ullah Mohammad
and
Ni, Rui
2021.
Experimental investigation of the acceleration statistics and added-mass force of deformable bubbles in intense turbulence.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 912,
Issue. ,
Li, Cheng
Panday, Rupendranath
Gao, Xi
Hong, Jiarong
and
Rogers, William A.
2021.
Measuring particle dynamics in a fluidized bed using digital in-line holography.
Chemical Engineering Journal,
Vol. 405,
Issue. ,
p.
126824.
Fox, Rodney O.
2021.
Advanced Approaches in Turbulence.
p.
307.
Masuk, Ashik Ullah Mohammad
Salibindla, Ashwanth K.R.
and
Ni, Rui
2021.
The orientational dynamics of deformable finite-sized bubbles in turbulence.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 915,
Issue. ,
Lafzi, Ali
and
Dabiri, Sadegh
2022.
A numerical lift force analysis on the inertial migration of a deformable droplet in steady and oscillatory microchannel flows.
Lab on a Chip,
Vol. 22,
Issue. 17,
p.
3245.
Gluzman, Igal
and
Thomas, Flint O.
2022.
Characterization of bubble dynamics in the nozzle flow of aviation fuels via computer vision tools.
International Journal of Multiphase Flow,
Vol. 154,
Issue. ,
p.
104133.
Mthethwa, P.
Workneh, T.S.
and
Kassim, A.
2022.
Small wind turbine blade optimisation and design using QBlade for integration into a low-cost fresh produce preservation technology.
Acta Horticulturae,
p.
417.
She, Wen-Xuan
Zuo, Zheng-Yu
Zhao, Hang
Gao, Qi
Zhang, Ling-Xin
and
Shao, Xue-Ming
2022.
Novel models for predicting the shape and motion of an ascending bubble in Newtonian liquids using machine learning.
Physics of Fluids,
Vol. 34,
Issue. 4,
Hassaini, Roumaissa
and
Coletti, Filippo
2022.
Scale-to-scale turbulence modification by small settling particles.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 949,
Issue. ,
Deike, Luc
2022.
Mass Transfer at the Ocean–Atmosphere Interface: The Role of Wave Breaking, Droplets, and Bubbles.
Annual Review of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 54,
Issue. 1,
p.
191.
Pandey, Vikash
Mitra, Dhrubaditya
and
Perlekar, Prasad
2022.
Turbulence modulation in buoyancy-driven bubbly flows.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 932,
Issue. ,
Tan, Shiyong
Zhong, Shijie
and
Ni, Rui
2023.
3D Lagrangian tracking of polydispersed bubbles at high image densities.
Experiments in Fluids,
Vol. 64,
Issue. 4,
Crialesi-Esposito, Marco
Scapin, Nicolò
Demou, Andreas D.
Rosti, Marco Edoardo
Costa, Pedro
Spiga, Filippo
and
Brandt, Luca
2023.
FluTAS: A GPU-accelerated finite difference code for multiphase flows.
Computer Physics Communications,
Vol. 284,
Issue. ,
p.
108602.
Subburaj, Rahul
Tang, Yali
and
Deen, Niels G.
2023.
An improved lift model for Euler-Lagrange simulations of bubble columns.
Chemical Engineering Science,
Vol. 265,
Issue. ,
p.
118182.
Yan, Sheng-lin
Wang, Xu-qing
Zhu, Li-tao
Zhang, Xi-bao
and
Luo, Zheng-hong
2023.
Mechanisms and modeling of bubble dynamic behaviors and mass transfer under gravity: A review.
Chemical Engineering Science,
Vol. 277,
Issue. ,
p.
118854.
Mei, Li
Chen, Xiaopeng
Liu, Bei
Zhang, Zhongyao
Hu, Tingting
Liang, Jiezhen
Wei, Xiaojie
and
Wang, Linlin
2023.
Experimental Study on Bubble Dynamics and Mass Transfer Characteristics of Coaxial Bubbles in Petroleum-Based Liquids.
ACS Omega,
Vol. 8,
Issue. 19,
p.
17159.
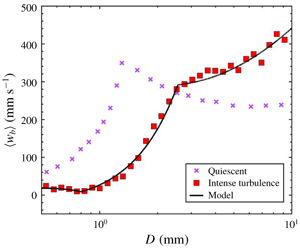
 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D716}\gtrsim 0.5~\text{m}^{2}~\text{s}^{-3}$. In contrast to a 30–40 % reduction in rise velocity previously reported in weak turbulence (the Weber number (
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D716}\gtrsim 0.5~\text{m}^{2}~\text{s}^{-3}$. In contrast to a 30–40 % reduction in rise velocity previously reported in weak turbulence (the Weber number ( $We$) is much smaller than the Eötvös number (
$We$) is much smaller than the Eötvös number ( $Eo$);
$Eo$);  $We\ll 1<Eo$), the bubble rise velocity in intense turbulence shows a surprising new behaviour: an abrupt transition from an order of magnitude slower to a factor of two faster than rising in an otherwise quiescent medium. This transition occurs when
$We\ll 1<Eo$), the bubble rise velocity in intense turbulence shows a surprising new behaviour: an abrupt transition from an order of magnitude slower to a factor of two faster than rising in an otherwise quiescent medium. This transition occurs when  $We$ increases from below one to above one, underscoring the key role played by the turbulence-induced deformation. We also formulate a model based on bubble–eddy coupling, and the results show an excellent agreement with not only our data in intense turbulence but also other works on weak turbulence. The model also helps us to extract the lift and drag coefficients of bubbles in intense turbulence for a wide range of
$We$ increases from below one to above one, underscoring the key role played by the turbulence-induced deformation. We also formulate a model based on bubble–eddy coupling, and the results show an excellent agreement with not only our data in intense turbulence but also other works on weak turbulence. The model also helps us to extract the lift and drag coefficients of bubbles in intense turbulence for a wide range of  $We$ and Reynolds numbers in situ.
$We$ and Reynolds numbers in situ.

