Published online by Cambridge University Press: 15 January 2019
Geophysical turbulence is observed to self-organize into large-scale flows such as zonal jets and coherent vortices. Previous studies of barotropic 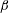 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FD}$-plane turbulence have shown that coherent flows emerge from a background of homogeneous turbulence as a bifurcation when the turbulence intensity increases. The emergence of large-scale flows has been attributed to a new type of collective, symmetry-breaking instability of the statistical state dynamics of the turbulent flow. In this work, we extend the analysis to stratified flows and investigate turbulent self-organization in a two-layer fluid without any imposed mean north–south thermal gradient and with turbulence supported by an external random stirring. We use a second-order closure of the statistical state dynamics, that is termed S3T, with an appropriate averaging ansatz that allows the identification of statistical turbulent equilibria and their structural stability. The bifurcation of the statistically homogeneous equilibrium state to inhomogeneous equilibrium states comprising zonal jets and/or large-scale waves when the energy input rate of the excitation passes a critical threshold is analytically studied. Our theory predicts that there is a large bias towards the emergence of barotropic flows. If the scale of excitation is of the order of (or larger than) the deformation radius, the large-scale structures are barotropic. Mixed barotropic–baroclinic states with jets and/or waves arise when the excitation is at scales shorter than the deformation radius with the baroclinic component of the flow being subdominant for low energy input rates and insignificant for higher energy input rates. The predictions of the S3T theory are compared with nonlinear simulations. The theory is found to accurately predict both the critical transition parameters and the scales of the emergent structures but underestimates their amplitude.
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FD}$-plane turbulence have shown that coherent flows emerge from a background of homogeneous turbulence as a bifurcation when the turbulence intensity increases. The emergence of large-scale flows has been attributed to a new type of collective, symmetry-breaking instability of the statistical state dynamics of the turbulent flow. In this work, we extend the analysis to stratified flows and investigate turbulent self-organization in a two-layer fluid without any imposed mean north–south thermal gradient and with turbulence supported by an external random stirring. We use a second-order closure of the statistical state dynamics, that is termed S3T, with an appropriate averaging ansatz that allows the identification of statistical turbulent equilibria and their structural stability. The bifurcation of the statistically homogeneous equilibrium state to inhomogeneous equilibrium states comprising zonal jets and/or large-scale waves when the energy input rate of the excitation passes a critical threshold is analytically studied. Our theory predicts that there is a large bias towards the emergence of barotropic flows. If the scale of excitation is of the order of (or larger than) the deformation radius, the large-scale structures are barotropic. Mixed barotropic–baroclinic states with jets and/or waves arise when the excitation is at scales shorter than the deformation radius with the baroclinic component of the flow being subdominant for low energy input rates and insignificant for higher energy input rates. The predictions of the S3T theory are compared with nonlinear simulations. The theory is found to accurately predict both the critical transition parameters and the scales of the emergent structures but underestimates their amplitude.