Crossref Citations
This article has been cited by the following publications. This list is generated based on data provided by
Crossref.
Zhou, Qi
and
Diamessis, Peter J.
2013.
Reflection of an internal gravity wave beam off a horizontal free-slip surface.
Physics of Fluids,
Vol. 25,
Issue. 3,
Pal, Anikesh
de Stadler, Matthew B.
and
Sarkar, Sutanu
2013.
The spatial evolution of fluctuations in a self-propelled wake compared to a patch of turbulence.
Physics of Fluids,
Vol. 25,
Issue. 9,
Munroe, James R.
and
Sutherland, Bruce R.
2014.
Internal wave energy radiated from a turbulent mixed layer.
Physics of Fluids,
Vol. 26,
Issue. 9,
Diamessis, P.J.
Wunsch, S.
Delwiche, I.
and
Richter, M.P.
2014.
Nonlinear generation of harmonics through the interaction of an internal wave beam with a model oceanic pycnocline.
Dynamics of Atmospheres and Oceans,
Vol. 66,
Issue. ,
p.
110.
Maffioli, Andrea
Davidson, P. A.
Dalziel, S. B.
and
Swaminathan, N.
2014.
The evolution of a stratified turbulent cloud.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 739,
Issue. ,
p.
229.
Bulatov, V. V.
and
Vladimirov, Yu. V.
2015.
Internal gravityWaves excited by a pulsating source of perturbations.
Fluid Dynamics,
Vol. 50,
Issue. 6,
p.
741.
Bulatov, V. V.
and
Vladimirov, Yu. V.
2015.
Far fields of internal gravity waves at arbitrary movement speeds of source of disturbances.
Izvestiya, Atmospheric and Oceanic Physics,
Vol. 51,
Issue. 6,
p.
609.
Pal, Anikesh
and
Sarkar, Sutanu
2015.
Effect of external turbulence on the evolution of a wake in stratified and unstratified environments.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 772,
Issue. ,
p.
361.
Brandt, A.
and
Rottier, J. R.
2015.
The internal wavefield generated by a towed sphere at low Froude number.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 769,
Issue. ,
p.
103.
Redford, J. A.
Lund, T. S.
and
Coleman, G. N.
2015.
A numerical study of a weakly stratified turbulent wake.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 776,
Issue. ,
p.
568.
Zhou, Qi
and
Diamessis, Peter J.
2015.
Lagrangian flows within reflecting internal waves at a horizontal free-slip surface.
Physics of Fluids,
Vol. 27,
Issue. 12,
Watanabe, T.
Riley, J. J.
and
Nagata, K.
2016.
Effects of stable stratification on turbulent/nonturbulent interfaces in turbulent mixing layers.
Physical Review Fluids,
Vol. 1,
Issue. 4,
Bulatov, V. V.
and
Vladimirov, Yu. V.
2016.
Far fields of internal gravitywaves generated by a perturbation source in a stratified rotating medium.
Fluid Dynamics,
Vol. 51,
Issue. 5,
p.
633.
Zhou, Qi
and
Diamessis, Peter J.
2016.
Surface manifestation of internal waves emitted by submerged localized stratified turbulence.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 798,
Issue. ,
p.
505.
Joshi, Sumedh M.
Thomsen, Greg N.
and
Diamessis, Peter J.
2016.
Deflation-accelerated preconditioning of the Poisson–Neumann Schur problem on long domains with a high-order discontinuous element-based collocation method.
Journal of Computational Physics,
Vol. 313,
Issue. ,
p.
209.
Watanabe, Tomoaki
Riley, James J.
de Bruyn Kops, Stephen M.
Diamessis, Peter J.
and
Zhou, Qi
2016.
Turbulent/non-turbulent interfaces in wakes in stably stratified fluids.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 797,
Issue. ,
Watanabe, T.
Riley, J. J.
and
Nagata, K.
2017.
Turbulent entrainment across turbulent-nonturbulent interfaces in stably stratified mixing layers.
Physical Review Fluids,
Vol. 2,
Issue. 10,
Pal, Anikesh
Sarkar, Sutanu
Posa, Antonio
and
Balaras, Elias
2017.
Direct numerical simulation of stratified flow past a sphere at a subcritical Reynolds number of 3700 and moderate Froude number.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 826,
Issue. ,
p.
5.
Bulatov, V.V.
and
Vladimirov, Yu.V.
2017.
Internal gravity waves excited by a pulsating perturbation source.
Journal of Applied Mathematics and Mechanics,
Vol. 81,
Issue. 5,
p.
384.
Bulatov, V. V.
and
Vladimirov, Yu. V.
2017.
Internal Gravity Waves Generated by an Oscillating Source of Perturbations Moving with Subcritical Velocity.
Journal of Applied Mechanics and Technical Physics,
Vol. 58,
Issue. 6,
p.
997.
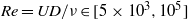 $\mathit{Re}= UD/ \nu \in [5\times 1{0}^{3} , 1{0}^{5} ] $ and internal Froude numbers,
$\mathit{Re}= UD/ \nu \in [5\times 1{0}^{3} , 1{0}^{5} ] $ and internal Froude numbers, 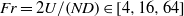 $\mathit{Fr}= 2U/ (ND)\in [4, 16, 64] $ (
$\mathit{Fr}= 2U/ (ND)\in [4, 16, 64] $ (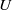 $U$,
$U$, 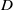 $D$ are characteristic body velocity and length scales, and
$D$ are characteristic body velocity and length scales, and 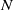 $N$ is the buoyancy frequency) is examined. At the higher
$N$ is the buoyancy frequency) is examined. At the higher 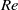 $\mathit{Re}$ examined, secondary Kelvin–Helmholtz instabilities and the resulting turbulent events, directly linked to a prolonged non-equilibrium (NEQ) regime in wake evolution, are responsible for IGW emission that persists up to
$\mathit{Re}$ examined, secondary Kelvin–Helmholtz instabilities and the resulting turbulent events, directly linked to a prolonged non-equilibrium (NEQ) regime in wake evolution, are responsible for IGW emission that persists up to 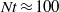 $Nt\approx 100$. In contrast, IGW emission at the lower
$Nt\approx 100$. In contrast, IGW emission at the lower 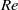 $\mathit{Re}$ investigated does not continue beyond
$\mathit{Re}$ investigated does not continue beyond 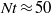 $Nt\approx 50$ for the three
$Nt\approx 50$ for the three  $\mathit{Fr}$ values considered. The horizontal wavelengths of the most energetic IGWs, obtained by continuous wavelet transforms, increase with
$\mathit{Fr}$ values considered. The horizontal wavelengths of the most energetic IGWs, obtained by continuous wavelet transforms, increase with 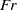 $\mathit{Fr}$ and appear to be smaller at the higher
$\mathit{Fr}$ and appear to be smaller at the higher 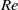 $\mathit{Re}$, especially at late times. The initial value of these wavelengths is set by the wake height at the beginning of the NEQ regime. At the lower
$\mathit{Re}$, especially at late times. The initial value of these wavelengths is set by the wake height at the beginning of the NEQ regime. At the lower 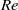 $\mathit{Re}$, consistent with a recently proposed model, the waves propagate over a narrow range of angles that minimize viscous decay along their path. At the higher
$\mathit{Re}$, consistent with a recently proposed model, the waves propagate over a narrow range of angles that minimize viscous decay along their path. At the higher 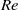 $\mathit{Re}$, wave motion is much less affected by viscosity, at least initially, and early-time wave propagation angles extend over a broader range of values which are linked to increased efficiency in momentum extraction from the turbulent wake source.
$\mathit{Re}$, wave motion is much less affected by viscosity, at least initially, and early-time wave propagation angles extend over a broader range of values which are linked to increased efficiency in momentum extraction from the turbulent wake source.

