Crossref Citations
This article has been cited by the following publications. This list is generated based on data provided by
Crossref.
Augier, Pierre
Galtier, Sébastien
and
Billant, Paul
2012.
Kolmogorov laws for stratified turbulence.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 709,
Issue. ,
p.
659.
Marino, R.
Mininni, P. D.
Rosenberg, D.
and
Pouquet, A.
2013.
Inverse cascades in rotating stratified turbulence: Fast growth of large scales.
EPL (Europhysics Letters),
Vol. 102,
Issue. 4,
p.
44006.
Waite, Michael L.
2013.
Potential enstrophy in stratified turbulence.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 722,
Issue. ,
Inamdar, Aniket R.
Lele, Sanjiva K.
and
Jacobson, Mark Z.
2013.
A Probabilistic Ice Habit Model for LES of Contrails.
Rorai, C.
Rosenberg, D.
Pouquet, A.
and
Mininni, P. D.
2013.
Helicity dynamics in stratified turbulence in the absence of forcing.
Physical Review E,
Vol. 87,
Issue. 6,
Bartello, P.
and
Tobias, S. M.
2013.
Sensitivity of stratified turbulence to the buoyancy Reynolds number.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 725,
Issue. ,
p.
1.
Herring, J R
and
Kimura, Y
2013.
Some issues and problems of stably stratified turbulence.
Physica Scripta,
Vol. T155,
Issue. ,
p.
014031.
Marino, Raffaele
Mininni, Pablo D.
Rosenberg, Duane
and
Pouquet, Annick
2013.
Emergence of helicity in rotating stratified turbulence.
Physical Review E,
Vol. 87,
Issue. 3,
Rorai, C.
Mininni, P. D.
and
Pouquet, A.
2014.
Turbulence comes in bursts in stably stratified flows.
Physical Review E,
Vol. 89,
Issue. 4,
Khani, Sina
and
Waite, Michael L.
2014.
Buoyancy scale effects in large-eddy simulations of stratified turbulence.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 754,
Issue. ,
p.
75.
Marino, R.
Mininni, P. D.
Rosenberg, D. L.
and
Pouquet, A.
2014.
Large-scale anisotropy in stably stratified rotating flows.
Physical Review E,
Vol. 90,
Issue. 2,
Paoli, R.
Thouron, O.
Escobar, J.
Picot, J.
and
Cariolle, D.
2014.
High-resolution large-eddy simulations of stably stratified flows: application to subkilometer-scale turbulence in the upper troposphere–lower stratosphere.
Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics,
Vol. 14,
Issue. 10,
p.
5037.
Waite, Michael L.
2014.
Modeling Atmospheric and Oceanic Flows.
p.
159.
Kumar, Abhishek
Chatterjee, Anando G.
and
Verma, Mahendra K.
2014.
Energy spectrum of buoyancy-driven turbulence.
Physical Review E,
Vol. 90,
Issue. 2,
Remmel, Mark
Sukhatme, Jai
and
Smith, Leslie M.
2014.
Nonlinear gravity-wave interactions in stratified turbulence.
Theoretical and Computational Fluid Dynamics,
Vol. 28,
Issue. 2,
p.
131.
Rosenberg, D.
Pouquet, A.
Marino, R.
and
Mininni, P. D.
2015.
Evidence for Bolgiano-Obukhov scaling in rotating stratified turbulence using high-resolution direct numerical simulations.
Physics of Fluids,
Vol. 27,
Issue. 5,
de Bruyn Kops, Stephen M.
2015.
Classical scaling and intermittency in strongly stratified Boussinesq turbulence.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 775,
Issue. ,
p.
436.
Sun, Jielun
Nappo, Carmen J.
Mahrt, Larry
Belušić, Danijel
Grisogono, Branko
Stauffer, David R.
Pulido, Manuel
Staquet, Chantal
Jiang, Qingfang
Pouquet, Annick
Yagüe, Carlos
Galperin, Boris
Smith, Ronald B.
Finnigan, John J.
Mayor, Shane D.
Svensson, Gunilla
Grachev, Andrey A.
and
Neff, William D.
2015.
Review of wave‐turbulence interactions in the stable atmospheric boundary layer.
Reviews of Geophysics,
Vol. 53,
Issue. 3,
p.
956.
Rorai, C.
Mininni, P. D.
and
Pouquet, A.
2015.
Stably stratified turbulence in the presence of large-scale forcing.
Physical Review E,
Vol. 92,
Issue. 1,
Augier, Pierre
Billant, Paul
and
Chomaz, Jean-Marc
2015.
Stratified turbulence forced with columnar dipoles: numerical study.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 769,
Issue. ,
p.
403.
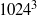 . Such resolution is sufficient to reveal inertial power-law ranges for suitably comprised horizontal and vertical spectra, which are designated as the wave and vortex mode (the Craya–Herring representation). We study mainly turbulence that is produced from randomly large-scale forcing via an Ornstein–Uhlenbeck process applied isotropically to the horizontal velocity field. In general, both the wave and vortex spectra are consistent with a Kolmogorov-like
. Such resolution is sufficient to reveal inertial power-law ranges for suitably comprised horizontal and vertical spectra, which are designated as the wave and vortex mode (the Craya–Herring representation). We study mainly turbulence that is produced from randomly large-scale forcing via an Ornstein–Uhlenbeck process applied isotropically to the horizontal velocity field. In general, both the wave and vortex spectra are consistent with a Kolmogorov-like  range at sufficiently large
range at sufficiently large 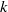 . At large scales, and for sufficiently strong stratification, the wave spectrum is a steeper
. At large scales, and for sufficiently strong stratification, the wave spectrum is a steeper 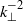 , while that for the vortex component is consistent with
, while that for the vortex component is consistent with 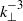 . Here
. Here 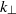 is the horizontally gathered wavenumber. In contrast to the horizontal wavenumber spectra, the vertical wavenumber spectra show very different features. For those spectra, a clear
is the horizontally gathered wavenumber. In contrast to the horizontal wavenumber spectra, the vertical wavenumber spectra show very different features. For those spectra, a clear 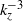 dependence for small scales is observed while the large scales show rather flat spectra. By modelling the horizontal layering of vorticity, we attempt to explain the flat spectra. These spectra are linked to two-point structure functions of the velocity correlations in the horizontal and vertical directions. We can observe the power-law transition also in certain of the two-point structure functions.
dependence for small scales is observed while the large scales show rather flat spectra. By modelling the horizontal layering of vorticity, we attempt to explain the flat spectra. These spectra are linked to two-point structure functions of the velocity correlations in the horizontal and vertical directions. We can observe the power-law transition also in certain of the two-point structure functions.