Crossref Citations
This article has been cited by the following publications. This list is generated based on data provided by
Crossref.
Sassun, David
Flores, Oscar
and
Orlandi, Paolo
2016.
Analysis and comparison between rough channel and pipe flows.
Journal of Physics: Conference Series,
Vol. 708,
Issue. ,
p.
012011.
Canton, Jacopo
Örlü, Ramis
Chin, Cheng
and
Schlatter, Philipp
2016.
Reynolds number dependence of large-scale friction control in turbulent channel flow.
Physical Review Fluids,
Vol. 1,
Issue. 8,
Stroh, A.
Hasegawa, Y.
Kriegseis, J.
and
Frohnapfel, B.
2016.
Secondary vortices over surfaces with spanwise varying drag.
Journal of Turbulence,
Vol. 17,
Issue. 12,
p.
1142.
Yang, Xiang I. A.
Sadique, Jasim
Mittal, Rajat
and
Meneveau, Charles
2016.
Exponential roughness layer and analytical model for turbulent boundary layer flow over rectangular-prism roughness elements.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 789,
Issue. ,
p.
127.
Tan, Yan Ming
and
Longmire, Ellen K.
2017.
Recovery of vortex packet organization in perturbed turbulent boundary layers.
Physical Review Fluids,
Vol. 2,
Issue. 10,
Benschop, H.O.G.
and
Breugem, W.-P.
2017.
Drag reduction by herringbone riblet texture in direct numerical simulations of turbulent channel flow.
Journal of Turbulence,
Vol. 18,
Issue. 8,
p.
717.
Chan, L
MacDonald, M
Chung, D
Hutchins, N
and
Ooi, A
2017.
Analysis of the coherent and turbulent stresses of a numerically simulated rough wall pipe.
Journal of Physics: Conference Series,
Vol. 822,
Issue. ,
p.
012011.
Vanderwel, C.
Placidi, M.
and
Ganapathisubramani, B.
2017.
Wind resource assessment in heterogeneous terrain.
Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences,
Vol. 375,
Issue. 2091,
p.
20160109.
Tomas, J. M.
Eisma, H. E.
Pourquie, M. J. B. M.
Elsinga, G. E.
Jonker, H. J. J.
and
Westerweel, J.
2017.
Pollutant Dispersion in Boundary Layers Exposed to Rural-to-Urban Transitions: Varying the Spanwise Length Scale of the Roughness.
Boundary-Layer Meteorology,
Vol. 163,
Issue. 2,
p.
225.
Squire, D. T.
Hutchins, N.
Morrill-Winter, C.
Schultz, M. P.
Klewicki, J. C.
and
Marusic, I.
2017.
Applicability of Taylor’s hypothesis in rough- and smooth-wall boundary layers.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 812,
Issue. ,
p.
398.
Kevin, Kevin
Monty, J. P.
Bai, H. L.
Pathikonda, G.
Nugroho, B.
Barros, J. M.
Christensen, K. T.
and
Hutchins, N.
2017.
Cross-stream stereoscopic particle image velocimetry of a modified turbulent boundary layer over directional surface pattern.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 813,
Issue. ,
p.
412.
Busse, A.
Thakkar, M.
and
Sandham, N. D.
2017.
Reynolds-number dependence of the near-wall flow over irregular rough surfaces.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 810,
Issue. ,
p.
196.
Hwang, Hyeon Gyu
and
Lee, Jae Hwa
2018.
Secondary flows in turbulent boundary layers over longitudinal surface roughness.
Physical Review Fluids,
Vol. 3,
Issue. 1,
Anderson, William
Yang, Jianzhi
Shrestha, Kalyan
and
Awasthi, Ankit
2018.
Turbulent secondary flows in wall turbulence: vortex forcing, scaling arguments, and similarity solution.
Environmental Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 18,
Issue. 6,
p.
1351.
Yang, Jianzhi
and
Anderson, William
2018.
Numerical Study of Turbulent Channel Flow over Surfaces with Variable Spanwise Heterogeneities: Topographically-driven Secondary Flows Affect Outer-layer Similarity of Turbulent Length Scales.
Flow, Turbulence and Combustion,
Vol. 100,
Issue. 1,
p.
1.
Bai, H. L.
Kevin
Hutchins, N.
and
Monty, J. P.
2018.
Turbulence modifications in a turbulent boundary layer over a rough wall with spanwise-alternating roughness strips.
Physics of Fluids,
Vol. 30,
Issue. 5,
Chung, D.
Monty, J. P.
and
Hutchins, N.
2018.
Similarity and structure of wall turbulence with lateral wall shear stress variations.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 847,
Issue. ,
p.
591.
Medjnoun, T.
Vanderwel, C.
and
Ganapathisubramani, B.
2018.
Characteristics of turbulent boundary layers over smooth surfaces with spanwise heterogeneities.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 838,
Issue. ,
p.
516.
Kurth, Sebastian
Hamann, Christian
Seume, Jörg R.
and
Mulleners, Karen
2018.
Experimental Investigation of the Influence of Anisotropic Surface Structures on the Boundary Layer Flow.
Awasthi, Ankit
and
Anderson, William
2018.
Numerical study of turbulent channel flow perturbed by spanwise topographic heterogeneity: Amplitude and frequency modulation within low- and high-momentum pathways.
Physical Review Fluids,
Vol. 3,
Issue. 4,
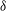 ${\it\delta}$, and do not appear for cases with finer spacing. Cases with coarser spacing also generate
${\it\delta}$, and do not appear for cases with finer spacing. Cases with coarser spacing also generate 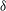 ${\it\delta}$-scale secondary flows with tertiary flows in the spaces in between. These results show that the ratio of the spanwise length scale of roughness heterogeneity to the boundary layer thickness is a critical parameter for the occurrence of these secondary motions in turbulent boundary layers over rough walls.
${\it\delta}$-scale secondary flows with tertiary flows in the spaces in between. These results show that the ratio of the spanwise length scale of roughness heterogeneity to the boundary layer thickness is a critical parameter for the occurrence of these secondary motions in turbulent boundary layers over rough walls.


