Crossref Citations
This article has been cited by the following publications. This list is generated based on data provided by
Crossref.
Long, Shen
Lau, Timothy C. W.
Chinnici, Alfonso
Tian, Zhao Feng
Dally, Bassam B.
and
Nathan, Graham J.
2017.
Experimental and numerical investigation of the iso-thermal flow characteristics within a cylindrical chamber with multiple planar-symmetric impinging jets.
Physics of Fluids,
Vol. 29,
Issue. 10,
Kueh, Kimberley C.Y.
Lau, Timothy C.W.
Nathan, Graham J.
and
Alwahabi, Zeyad T.
2017.
Single-shot planar temperature imaging of radiatively heated fluidized particles.
Optics Express,
Vol. 25,
Issue. 23,
p.
28764.
Mullyadzhanov, R. I.
Sandberg, R. D.
Abdurakipov, S. S.
George, W. K.
and
Hanjalić, K.
2018.
Propagating helical waves as a building block of round turbulent jets.
Physical Review Fluids,
Vol. 3,
Issue. 6,
Dalla Barba, Federico
and
Picano, Francesco
2018.
Clustering and entrainment effects on the evaporation of dilute droplets in a turbulent jet.
Physical Review Fluids,
Vol. 3,
Issue. 3,
Long, Shen
Lau, Timothy C. W.
Chinnici, Alfonso
Tian, Zhao Feng
Dally, Bassam B.
and
Nathan, Graham J.
2018.
The influence of aspect ratio on the iso-thermal flow characteristics of multiple confined jets.
Physics of Fluids,
Vol. 30,
Issue. 12,
p.
125108.
Meyer, M.
Caruso, F.
and
Lupoi, R.
2018.
Particle velocity and dispersion of high Stokes number particles by PTV measurements inside a transparent supersonic Cold Spray nozzle.
International Journal of Multiphase Flow,
Vol. 106,
Issue. ,
p.
296.
Borup, Daniel D.
Elkins, Christopher J.
and
Eaton, John K.
2018.
Development and validation of an MRI-based method for 3D particle concentration measurement.
International Journal of Heat and Fluid Flow,
Vol. 71,
Issue. ,
p.
275.
Zhang, Wei
Tainaka, Kazuki
Ahn, Seongyool
Watanabe, Hiroaki
and
Kitagawa, Toshiaki
2018.
Experimental and numerical investigation of effects of particle shape and size distribution on particles’ dispersion in a coaxial jet flow.
Advanced Powder Technology,
Vol. 29,
Issue. 10,
p.
2322.
Battista, F.
Gualtieri, P.
Mollicone, J.-P.
and
Casciola, C.M.
2018.
Application of the Exact Regularized Point Particle method (ERPP) to particle laden turbulent shear flows in the two-way coupling regime.
International Journal of Multiphase Flow,
Vol. 101,
Issue. ,
p.
113.
Mollicone, J.-P.
Sharifi, M.
Battista, F.
Gualtieri, P.
and
Casciola, C. M.
2019.
Particles in turbulent separated flow over a bump: Effect of the Stokes number and lift force.
Physics of Fluids,
Vol. 31,
Issue. 10,
Feng, Lele
Zhang, Qi
Wu, Yuxin
Huang, Wenshi
and
Zhang, Hai
2019.
Theoretical Analysis on the Criteria of MILD Coal Combustion.
Energy & Fuels,
Vol. 33,
Issue. 11,
p.
11923.
Lau, Timothy C. W.
Frank, Jonathan H.
and
Nathan, Graham J.
2019.
Resolving the three-dimensional structure of particles that are aerodynamically clustered by a turbulent flow.
Physics of Fluids,
Vol. 31,
Issue. 7,
Davis, Dominic
Troiano, Maurizio
Chinnici, Alfonso
Saw, Woei L.
Lau, Timothy
Solimene, Roberto
Salatino, Piero
and
Nathan, Graham J.
2019.
Particle residence time distributions in a vortex-based solar particle receiver-reactor: The influence of receiver tilt angle.
Solar Energy,
Vol. 190,
Issue. ,
p.
126.
Battista, F.
Mollicone, J.-P.
Gualtieri, P.
Messina, R.
and
Casciola, C. M.
2019.
Exact regularised point particle (ERPP) method for particle-laden wall-bounded flows in the two-way coupling regime.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 878,
Issue. ,
p.
420.
Kim, Taehoon
Ni, Rui
Capecelatro, Jesse
Yao, Yuan
Shallcross, Gregory S.
Mehta, Manish
and
Rabinovitch, Jason
2020.
The dynamics of inertial particles in underexpanded jets: An experimental study.
Davis, Dominic
Troiano, Maurizio
Chinnici, Alfonso
Saw, Woei L.
Lau, Timothy
Solimene, Roberto
Salatino, Piero
and
Nathan, Graham J.
2020.
Particle residence time distributions in a vortex-based solar particle receiver-reactor: An experimental, numerical and theoretical study.
Chemical Engineering Science,
Vol. 214,
Issue. ,
p.
115421.
Wang, Jingyu
Huang, Wenshi
Zhang, Yang
Wu, Yuxin
Zhang, Hai
and
Yue, Guangxi
2020.
Particle trajectories in pipe flow considering particle–wall collisions.
Physics of Fluids,
Vol. 32,
Issue. 4,
Mena, Sarah E.
and
Curtis, Jennifer Sinclair
2020.
Experimental data for solid–liquid flows at intermediate and high Stokes numbers.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 883,
Issue. ,
Kubler, R.F.
Rotinat, R.
Badreddine, J.
and
Puydt, Q.
2020.
Experimental Analysis of the Shot Peening Particle Stream Using Particle Tracking and Digital Image Correlation Techniques.
Experimental Mechanics,
Vol. 60,
Issue. 4,
p.
429.
Lewis, Elliott W.
Lau, Timothy C. W.
Sun, Zhiwei
Alwahabi, Zeyad T.
and
Nathan, Graham J.
2020.
Luminescence interference to two-colour toluene laser-induced fluorescence thermometry in a particle-laden flow.
Experiments in Fluids,
Vol. 61,
Issue. 4,
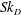 $Sk_{D}$, was systematically varied over two orders of magnitude between 0.3 and 22.4, while the Reynolds number was maintained in the turbulent regime (
$Sk_{D}$, was systematically varied over two orders of magnitude between 0.3 and 22.4, while the Reynolds number was maintained in the turbulent regime (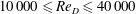 $10\,000\leqslant Re_{D}\leqslant 40\,000$). The mass loading was fixed at
$10\,000\leqslant Re_{D}\leqslant 40\,000$). The mass loading was fixed at 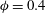 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D719}=0.4$, resulting in a flow that is in the two-way coupling regime. The results show that, in contrast to all previous work where a single Stokes number has been used to characterise fluid–particle interactions, the characteristic Stokes number in the axial direction is lower than that for the radial direction. This is attributed to the significantly greater length scales in the axial motions than in the radial ones. It further leads to a preferential response of particles to gas-phase axial velocity fluctuations,
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D719}=0.4$, resulting in a flow that is in the two-way coupling regime. The results show that, in contrast to all previous work where a single Stokes number has been used to characterise fluid–particle interactions, the characteristic Stokes number in the axial direction is lower than that for the radial direction. This is attributed to the significantly greater length scales in the axial motions than in the radial ones. It further leads to a preferential response of particles to gas-phase axial velocity fluctuations, 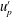 $u_{p}^{\prime }$, over radial velocity fluctuations,
$u_{p}^{\prime }$, over radial velocity fluctuations, 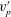 $v_{p}^{\prime }$. This, in turn, leads to high levels of anisotropy in the particle-phase velocity fluctuations,
$v_{p}^{\prime }$. This, in turn, leads to high levels of anisotropy in the particle-phase velocity fluctuations, 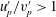 $u_{p}^{\prime }/v_{p}^{\prime }>1$, throughout the jet, with
$u_{p}^{\prime }/v_{p}^{\prime }>1$, throughout the jet, with 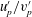 $u_{p}^{\prime }/v_{p}^{\prime }$ increasing as
$u_{p}^{\prime }/v_{p}^{\prime }$ increasing as 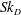 $Sk_{D}$ is increased. The results also show that the region within the first few diameters of the exit plane is characterised by a process of particle reorganisation, resulting in significant particle migration to the jet axis for
$Sk_{D}$ is increased. The results also show that the region within the first few diameters of the exit plane is characterised by a process of particle reorganisation, resulting in significant particle migration to the jet axis for 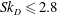 $Sk_{D}\leqslant 2.8$ and away from the axis for
$Sk_{D}\leqslant 2.8$ and away from the axis for 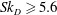 $Sk_{D}\geqslant 5.6$. This migration, together with particle deceleration along the axis, causes local humps in the centreline concentration whose value can even exceed those at the exit plane.
$Sk_{D}\geqslant 5.6$. This migration, together with particle deceleration along the axis, causes local humps in the centreline concentration whose value can even exceed those at the exit plane.


