Article contents
Chaotic advection in a steady, three-dimensional, Ekman-driven eddy
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 05 December 2013
Abstract
We investigate and quantify stirring due to chaotic advection within a steady, three-dimensional, Ekman-driven, rotating cylinder flow. The flow field has vertical overturning and horizontal swirling motion, and is an idealization of motion observed in some ocean eddies. The flow is characterized by strong background rotation, and we explore variations in Ekman and Rossby numbers, 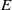 $E$ and
$E$ and 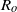 ${R}_{o} $, over ranges appropriate for the ocean mesoscale and submesoscale. A high-resolution spectral element model is used in conjunction with linear analytical theory, weakly nonlinear resonance analysis and a kinematic model in order to map out the barriers, manifolds, resonance layers and other objects that provide a template for chaotic stirring. As expected, chaos arises when a radially symmetric background state is perturbed by a symmetry-breaking disturbance. In the background state, each trajectory lives on a torus and some of the latter survive the perturbation and act as barriers to chaotic transport, a result consistent with an extension of the KAM theorem for three-dimensional, volume-preserving flow. For shallow eddies, where
${R}_{o} $, over ranges appropriate for the ocean mesoscale and submesoscale. A high-resolution spectral element model is used in conjunction with linear analytical theory, weakly nonlinear resonance analysis and a kinematic model in order to map out the barriers, manifolds, resonance layers and other objects that provide a template for chaotic stirring. As expected, chaos arises when a radially symmetric background state is perturbed by a symmetry-breaking disturbance. In the background state, each trajectory lives on a torus and some of the latter survive the perturbation and act as barriers to chaotic transport, a result consistent with an extension of the KAM theorem for three-dimensional, volume-preserving flow. For shallow eddies, where  $E$ is
$E$ is 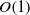 $O(1)$, the flow is dominated by thin resonant layers sandwiched between KAM-type barriers, and the stirring rate is weak. On the other hand, eddies with moderately small
$O(1)$, the flow is dominated by thin resonant layers sandwiched between KAM-type barriers, and the stirring rate is weak. On the other hand, eddies with moderately small 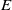 $E$ experience thicker resonant layers, wider-spread chaos and much more rapid stirring. This trend reverses for sufficiently small
$E$ experience thicker resonant layers, wider-spread chaos and much more rapid stirring. This trend reverses for sufficiently small 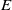 $E$, corresponding to deep eddies, where the vertical rigidity imposed by strong rotation limits the stirring. The bulk stirring rate, estimated from a passive tracer release, confirms the non-monotonic variation in stirring rate with
$E$, corresponding to deep eddies, where the vertical rigidity imposed by strong rotation limits the stirring. The bulk stirring rate, estimated from a passive tracer release, confirms the non-monotonic variation in stirring rate with 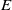 $E$. This result is shown to be consistent with linear Ekman layer theory in conjunction with a resonant width calculation and the Taylor–Proudman theorem. The theory is able to roughly predict the value of
$E$. This result is shown to be consistent with linear Ekman layer theory in conjunction with a resonant width calculation and the Taylor–Proudman theorem. The theory is able to roughly predict the value of 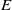 $E$ at which stirring is maximum. For large disturbances, the stirring rate becomes monotonic over the range of Ekman numbers explored. We also explore variation in the eddy aspect ratio.
$E$ at which stirring is maximum. For large disturbances, the stirring rate becomes monotonic over the range of Ekman numbers explored. We also explore variation in the eddy aspect ratio.
- Type
- Papers
- Information
- Copyright
- ©2013 Cambridge University Press
References
- 20
- Cited by


