Article contents
Cavitation structures formed during the collision of a sphere with an ultra-viscous wetted surface
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 05 May 2016
Abstract
We investigate the inception of cavitation and resulting structures when a sphere collides with a solid surface covered with a layer of non-Newtonian liquid having a kinematic viscosity of up to 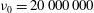 ${\it\nu}_{0}=20\,000\,000$ cSt. We show the existence of shear-stress-induced cavitation during sphere approach towards the base wall (i.e. the pressurization stage) in ultra-viscous films using a synchronized dual-view high-speed imaging system. For the experimental parameters employed, liquids having viscoelastic properties of
${\it\nu}_{0}=20\,000\,000$ cSt. We show the existence of shear-stress-induced cavitation during sphere approach towards the base wall (i.e. the pressurization stage) in ultra-viscous films using a synchronized dual-view high-speed imaging system. For the experimental parameters employed, liquids having viscoelastic properties of 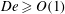 $De\geqslant O(1)$ are shown to enable sphere rebound without any prior contact with the solid wall. Cavitation by depressurization (i.e. during rebound) in such non-contact cases is observed to onset after a noticeable delay from when the minimum gap distance is reached. Also, the cavities created originate from remnant bubbles, being the remains of the primary bubble entrapment formed by the lubrication pressure of the air during film entry. Cases where physical contact occurs (contact cases) in 10 000 cSt
$De\geqslant O(1)$ are shown to enable sphere rebound without any prior contact with the solid wall. Cavitation by depressurization (i.e. during rebound) in such non-contact cases is observed to onset after a noticeable delay from when the minimum gap distance is reached. Also, the cavities created originate from remnant bubbles, being the remains of the primary bubble entrapment formed by the lubrication pressure of the air during film entry. Cases where physical contact occurs (contact cases) in 10 000 cSt 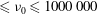 ${\leqslant}{\it\nu}_{0}\leqslant 1000\,000$ cSt films produce cavities attached to the base wall, which extend into an hourglass shape. In contrast, strikingly different structures occur in the most viscous liquids due to the disproportionality in radial expansion and longitudinal extension along the cavity length. Horizontal shear rates calculated using particle image velocimetry (PIV) measurements show the apparent fluid viscosity to vary substantially as the sphere approaches and rebounds away from the base wall. A theoretical model based on the lubrication assumption is solved for the squeeze flow in the regime identified for shear-induced cavity events, to investigate the criterion for cavity inception in further detail.
${\leqslant}{\it\nu}_{0}\leqslant 1000\,000$ cSt films produce cavities attached to the base wall, which extend into an hourglass shape. In contrast, strikingly different structures occur in the most viscous liquids due to the disproportionality in radial expansion and longitudinal extension along the cavity length. Horizontal shear rates calculated using particle image velocimetry (PIV) measurements show the apparent fluid viscosity to vary substantially as the sphere approaches and rebounds away from the base wall. A theoretical model based on the lubrication assumption is solved for the squeeze flow in the regime identified for shear-induced cavity events, to investigate the criterion for cavity inception in further detail.
- Type
- Papers
- Information
- Copyright
- © 2016 Cambridge University Press
References
Mansoor et al. supplementary movie
Side (left) and bottom (right) views of the impact and rebound of a tungsten sphere in a 5 mm-thick layer of 100,000 cSt oil. The impact speeds are (a) 2.78 m/s and (b) 3.42 m/s giving St = 0.94 and 1.16 and De = 1.59 and 1.95, respectively.
Mansoor et al. supplementary movie
Side-views of cavity structures forming during the rebound of a sphere from a 5 mm=thick layers of 20,000,000 cSt oil. The impact speeds are 5.51, 5.59 and 5.77 m/s respectively, giving St = O(10-2) and De = O(400).
- 10
- Cited by



