Article contents
Wall effects on pressure fluctuations in turbulent channel flow
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 27 February 2013
Abstract
The purpose of the present paper is to study the influence of wall echo on pressure fluctuations 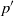 ${p}^{\prime } $, and on statistical correlations containing
${p}^{\prime } $, and on statistical correlations containing 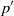 ${p}^{\prime } $, namely, redistribution
${p}^{\prime } $, namely, redistribution 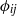 ${\phi }_{ij} $, pressure diffusion
${\phi }_{ij} $, pressure diffusion 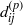 ${ d}_{ij}^{(p)} $ and velocity pressure-gradient
${ d}_{ij}^{(p)} $ and velocity pressure-gradient 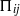 ${\Pi }_{ij} $. We extend the usual analysis of turbulent correlations containing pressure fluctuations in wall-bounded direct numerical simulations (Kim, J. Fluid Mech., vol. 205, 1989, pp. 421–451), separating
${\Pi }_{ij} $. We extend the usual analysis of turbulent correlations containing pressure fluctuations in wall-bounded direct numerical simulations (Kim, J. Fluid Mech., vol. 205, 1989, pp. 421–451), separating 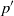 ${p}^{\prime } $ not only into rapid
${p}^{\prime } $ not only into rapid 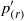 ${ p}_{(r)}^{\prime } $ and slow
${ p}_{(r)}^{\prime } $ and slow 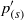 ${ p}_{(s)}^{\prime } $ parts (Chou, Q. Appl. Maths, vol. 3, 1945, pp. 38–54), but also further into volume (
${ p}_{(s)}^{\prime } $ parts (Chou, Q. Appl. Maths, vol. 3, 1945, pp. 38–54), but also further into volume (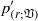 ${ p}_{(r; \mathfrak{V})}^{\prime } $ and
${ p}_{(r; \mathfrak{V})}^{\prime } $ and 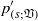 ${ p}_{(s; \mathfrak{V})}^{\prime } $) and surface (wall echo,
${ p}_{(s; \mathfrak{V})}^{\prime } $) and surface (wall echo, 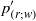 ${ p}_{(r; w)}^{\prime } $ and
${ p}_{(r; w)}^{\prime } $ and 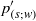 ${ p}_{(s; w)}^{\prime } $) terms. An algorithm, based on a Green’s function approach, is developed to compute the above splittings for various correlations containing pressure fluctuations (redistribution, pressure diffusion, velocity pressure-gradient), in fully developed turbulent plane channel flow. This exact analysis confirms previous results based on a method-of-images approximation (Manceau, Wang & Laurence, J. Fluid Mech., vol. 438, 2001, pp. 307–338) showing that, at the wall,
${ p}_{(s; w)}^{\prime } $) terms. An algorithm, based on a Green’s function approach, is developed to compute the above splittings for various correlations containing pressure fluctuations (redistribution, pressure diffusion, velocity pressure-gradient), in fully developed turbulent plane channel flow. This exact analysis confirms previous results based on a method-of-images approximation (Manceau, Wang & Laurence, J. Fluid Mech., vol. 438, 2001, pp. 307–338) showing that, at the wall, 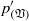 ${ p}_{(\mathfrak{V})}^{\prime } $ and
${ p}_{(\mathfrak{V})}^{\prime } $ and 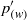 ${ p}_{(w)}^{\prime } $ are usually of the same sign and approximately equal. The above results are then used to study the contribution of each mechanism to the pressure correlations in low-Reynolds-number plane channel flow, and to discuss standard second-moment-closure modelling practices.
${ p}_{(w)}^{\prime } $ are usually of the same sign and approximately equal. The above results are then used to study the contribution of each mechanism to the pressure correlations in low-Reynolds-number plane channel flow, and to discuss standard second-moment-closure modelling practices.
- Type
- Papers
- Information
- Copyright
- ©2013 Cambridge University Press
References
- 31
- Cited by


