Published online by Cambridge University Press: 06 September 2019
We present an investigation of the root-mean-square (r.m.s.) temperature 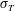 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D70E}_{T}$ and the r.m.s. velocity
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D70E}_{T}$ and the r.m.s. velocity 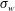 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D70E}_{w}$ in the bulk of Rayleigh–Bénard turbulence, using new experimental data from the current study and experimental and numerical data from previous studies. We find that, once scaled by the convective temperature
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D70E}_{w}$ in the bulk of Rayleigh–Bénard turbulence, using new experimental data from the current study and experimental and numerical data from previous studies. We find that, once scaled by the convective temperature 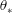 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{\ast }$, the value of
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{\ast }$, the value of 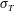 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D70E}_{T}$ at the cell centre is a constant (
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D70E}_{T}$ at the cell centre is a constant (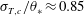 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D70E}_{T,c}/\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{\ast }\approx 0.85$) over a wide range of the Rayleigh number (
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D70E}_{T,c}/\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{\ast }\approx 0.85$) over a wide range of the Rayleigh number (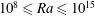 $10^{8}\leqslant Ra\leqslant 10^{15}$) and the Prandtl number (
$10^{8}\leqslant Ra\leqslant 10^{15}$) and the Prandtl number (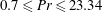 $0.7\leqslant Pr\leqslant 23.34$), and is independent of the surface topographies of the top and bottom plates of the convection cell. A constant close to unity suggests that
$0.7\leqslant Pr\leqslant 23.34$), and is independent of the surface topographies of the top and bottom plates of the convection cell. A constant close to unity suggests that 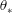 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{\ast }$ is a proper measure of the temperature fluctuation in the core region. On the other hand,
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{\ast }$ is a proper measure of the temperature fluctuation in the core region. On the other hand, 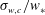 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D70E}_{w,c}/w_{\ast }$, the vertical r.m.s. velocity at the cell centre scaled by the convective velocity
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D70E}_{w,c}/w_{\ast }$, the vertical r.m.s. velocity at the cell centre scaled by the convective velocity 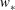 $w_{\ast }$, shows a weak
$w_{\ast }$, shows a weak 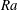 $Ra$-dependence (
$Ra$-dependence (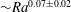 ${\sim}Ra^{0.07\pm 0.02}$) over
${\sim}Ra^{0.07\pm 0.02}$) over 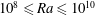 $10^{8}\leqslant Ra\leqslant 10^{10}$ at
$10^{8}\leqslant Ra\leqslant 10^{10}$ at 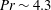 $Pr\sim 4.3$ and is independent of plate topography. Similar to a previous finding by He & Xia (Phys. Rev. Lett., vol. 122, 2019, 014503), we find that the r.m.s. temperature profile
$Pr\sim 4.3$ and is independent of plate topography. Similar to a previous finding by He & Xia (Phys. Rev. Lett., vol. 122, 2019, 014503), we find that the r.m.s. temperature profile 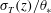 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D70E}_{T}(z)/\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{\ast }$ in the region of the mixing zone with a mean horizontal shear exhibits a power-law dependence on the distance
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D70E}_{T}(z)/\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{\ast }$ in the region of the mixing zone with a mean horizontal shear exhibits a power-law dependence on the distance  $z$ from the plate, but now the universal profile applies to both smooth and rough surface topographies and over a wider range of
$z$ from the plate, but now the universal profile applies to both smooth and rough surface topographies and over a wider range of 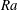 $Ra$. The vertical r.m.s. velocity profile
$Ra$. The vertical r.m.s. velocity profile 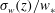 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D70E}_{w}(z)/w_{\ast }$ obeys a logarithmic dependence on
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D70E}_{w}(z)/w_{\ast }$ obeys a logarithmic dependence on  $z$. The study thus demonstrates that the typical scales for the temperature and the velocity are the convective temperature
$z$. The study thus demonstrates that the typical scales for the temperature and the velocity are the convective temperature 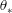 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{\ast }$ and the convective velocity
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{\ast }$ and the convective velocity 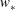 $w_{\ast }$, respectively. Finally, we note that
$w_{\ast }$, respectively. Finally, we note that 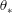 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{\ast }$ may be utilised to study the flow regime transitions in ultrahigh-
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}_{\ast }$ may be utilised to study the flow regime transitions in ultrahigh-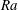 $Ra$-number turbulent convection.
$Ra$-number turbulent convection.