Article contents
Scaling laws for migrating cloud of low-Reynolds-number particles with Coulomb repulsion
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 28 November 2017
Abstract
We investigate the evolution of spherical clouds of charged particles that migrate under the action of a uniform external electrostatic field. Hydrodynamic interactions are modelled by Oseen equations and the Coulomb repulsion is calculated through pairwise summation. It is shown that strong long-range Coulomb repulsion can prevent the breakup of the clouds covering a wide range of particle Reynolds number 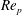 $Re_{p}$ and cloud-to-particle size ratio
$Re_{p}$ and cloud-to-particle size ratio 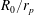 $R_{0}/r_{p}$. A dimensionless charge parameter
$R_{0}/r_{p}$. A dimensionless charge parameter 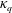 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D705}_{q}$ is constructed to quantify the effect of the repulsion, and a critical value
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D705}_{q}$ is constructed to quantify the effect of the repulsion, and a critical value 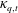 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D705}_{q,t}$ is deduced, which successfully captures the transition of a cloud from hydrodynamically controlled regime to repulsion-controlled regime. Our results also reveal that, with sufficiently strong repulsion, the cloud undergoes a universal self-similar expansion. Scaling laws of cloud radius
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D705}_{q,t}$ is deduced, which successfully captures the transition of a cloud from hydrodynamically controlled regime to repulsion-controlled regime. Our results also reveal that, with sufficiently strong repulsion, the cloud undergoes a universal self-similar expansion. Scaling laws of cloud radius 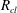 $R_{cl}$ and particle number density
$R_{cl}$ and particle number density  $n$ are obtained by solving a continuum convection equation.
$n$ are obtained by solving a continuum convection equation.
- Type
- JFM Papers
- Information
- Copyright
- © 2017 Cambridge University Press
References
- 12
- Cited by



