Crossref Citations
This article has been cited by the following publications. This list is generated based on data provided by
Crossref.
Gustavsson, K.
Jucha, J.
Naso, A.
Lévêque, E.
Pumir, A.
and
Mehlig, B.
2017.
Statistical Model for the Orientation of Nonspherical Particles Settling in Turbulence.
Physical Review Letters,
Vol. 119,
Issue. 25,
Pujara, Nimish
and
Variano, Evan A.
2017.
Rotations of small, inertialess triaxial ellipsoids in isotropic turbulence.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 821,
Issue. ,
p.
517.
Fries, J.
Kumar, M. Vijay
Mihiretie, B. Mekonnen
Hanstorp, D.
and
Mehlig, B.
2018.
Spinning and tumbling of micron-sized triangles in a micro-channel shear flow.
Physics of Fluids,
Vol. 30,
Issue. 3,
Bounoua, S.
Bouchet, G.
and
Verhille, G.
2018.
Tumbling of Inertial Fibers in Turbulence.
Physical Review Letters,
Vol. 121,
Issue. 12,
Pujara, Nimish
Oehmke, Theresa B.
Bordoloi, Ankur D.
and
Variano, Evan A.
2018.
Rotations of large inertial cubes, cuboids, cones, and cylinders in turbulence.
Physical Review Fluids,
Vol. 3,
Issue. 5,
Pujara, Nimish
Voth, Greg A.
and
Variano, Evan A.
2019.
Scale-dependent alignment, tumbling and stretching of slender rods in isotropic turbulence.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 860,
Issue. ,
p.
465.
Kuperman, Sofia
Sabban, Lilach
and
van Hout, René
2019.
Inertial effects on the dynamics of rigid heavy fibers in isotropic turbulence.
Physical Review Fluids,
Vol. 4,
Issue. 6,
Wang, Yayun
Sierakowski, Adam
and
Prosperetti, Andrea
2019.
Rotational dynamics of a particle in a turbulent stream.
Physical Review Fluids,
Vol. 4,
Issue. 6,
Chen, Xi
Zhong, Wenqi
and
Heindel, Theodore J.
2019.
Using stereo XPTV to determine cylindrical particle distribution and velocity in a binary fluidized bed.
AIChE Journal,
Vol. 65,
Issue. 2,
p.
520.
Schneiders, Lennart
Fröhlich, Konstantin
Meinke, Matthias
and
Schröder, Wolfgang
2019.
The decay of isotropic turbulence carrying non-spherical finite-size particles.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 875,
Issue. ,
p.
520.
DiBenedetto, Michelle H.
Koseff, Jeffrey R.
and
Ouellette, Nicholas T.
2019.
Orientation dynamics of nonspherical particles under surface gravity waves.
Physical Review Fluids,
Vol. 4,
Issue. 3,
Shaik, Subhani
Kuperman, Sofia
Rinsky, Vladislav
and
van Hout, René
2020.
Measurements of length effects on the dynamics of rigid fibers in a turbulent channel flow.
Physical Review Fluids,
Vol. 5,
Issue. 11,
Bordoloi, Ankur D.
Variano, Evan
and
Verhille, Gautier
2020.
Lagrangian Time Scale of Passive Rotation for Mesoscale Particles in Turbulence.
Frontiers in Marine Science,
Vol. 7,
Issue. ,
Bordoloi, Ankur D.
Lai, Chris C. K.
Clark, Laura
Carrillo, Gerardo V.
and
Variano, Evan
2020.
Turbulence statistics in a negatively buoyant multiphase plume.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 896,
Issue. ,
Rosti, Marco E.
Olivieri, Stefano
Banaei, Arash A.
Brandt, Luca
and
Mazzino, Andrea
2020.
Flowing fibers as a proxy of turbulence statistics.
Meccanica,
Vol. 55,
Issue. 2,
p.
357.
Yousefi, Ali
Niazi Ardekani, Mehdi
and
Brandt, Luca
2020.
Modulation of turbulence by finite-size particles in statistically steady-state homogeneous shear turbulence.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 899,
Issue. ,
Oehmke, Theresa B.
and
Variano, Evan A.
2021.
A new particle for measuring mass transfer in turbulence.
Experiments in Fluids,
Vol. 62,
Issue. 1,
Brizzolara, Stefano
Rosti, Marco Edoardo
Olivieri, Stefano
Brandt, Luca
Holzner, Markus
and
Mazzino, Andrea
2021.
Fiber Tracking Velocimetry for Two-Point Statistics of Turbulence.
Physical Review X,
Vol. 11,
Issue. 3,
Cabrera, Facundo
and
Cobelli, Pablo J.
2021.
Design, construction and validation of an instrumented particle for the Lagrangian characterization of flows.
Experiments in Fluids,
Vol. 62,
Issue. 1,
Oehmke, Theresa B.
Bordoloi, Ankur D.
Variano, Evan
and
Verhille, Gautier
2021.
Spinning and tumbling of long fibers in isotropic turbulence.
Physical Review Fluids,
Vol. 6,
Issue. 4,
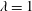 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D706}=1$) are considered, with size
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D706}=1$) are considered, with size 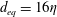 $d_{eq}=16\unicode[STIX]{x1D702}$,
$d_{eq}=16\unicode[STIX]{x1D702}$, 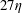 $27\unicode[STIX]{x1D702}$ and
$27\unicode[STIX]{x1D702}$ and 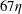 $67\unicode[STIX]{x1D702}$. Here,
$67\unicode[STIX]{x1D702}$. Here, 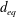 $d_{eq}$ is the diameter of a sphere whose volume is equal to that of the particle and
$d_{eq}$ is the diameter of a sphere whose volume is equal to that of the particle and 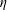 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D702}$ is the Kolmogorov length scale. Results show that the variance of the particle rotation rate follows a
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D702}$ is the Kolmogorov length scale. Results show that the variance of the particle rotation rate follows a 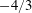 $-4/3$ power-law scaling with respect to
$-4/3$ power-law scaling with respect to 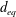 $d_{eq}$. To examine the effect of particle shape, two cylinders with identical volumes and different aspect ratios (
$d_{eq}$. To examine the effect of particle shape, two cylinders with identical volumes and different aspect ratios (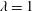 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D706}=1$ and
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D706}=1$ and 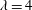 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D706}=4$) are measured. Their motion also scales with
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D706}=4$) are measured. Their motion also scales with 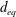 $d_{eq}$ regardless of shape. Simultaneous measurements of orientation and rotation for
$d_{eq}$ regardless of shape. Simultaneous measurements of orientation and rotation for 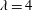 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D706}=4$ particles allows a decomposition of rotation along the primary axes of each particle. This analysis shows that there is no preference for rotation about a particle’s symmetry axis, unlike the preference displayed by sub-Kolmogorov-scale particles in previous studies.
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D706}=4$ particles allows a decomposition of rotation along the primary axes of each particle. This analysis shows that there is no preference for rotation about a particle’s symmetry axis, unlike the preference displayed by sub-Kolmogorov-scale particles in previous studies.


