Crossref Citations
This article has been cited by the following publications. This list is generated based on data provided by
Crossref.
Wang, Jia-song
Fan, Dixia
and
Lin, Ke
2020.
A review on flow-induced vibration of offshore circular cylinders.
Journal of Hydrodynamics,
Vol. 32,
Issue. 3,
p.
415.
Chen, Weilin
Ji, Chunning
Xu, Dong
and
Zhang, Zhimeng
2020.
Oscillation regimes and mechanisms in the vortex-induced vibrations of three circular cylinders with equilateral-triangular arrangements.
Physics of Fluids,
Vol. 32,
Issue. 4,
Yan, Yuhao
Ji, Chunning
and
Srinil, Narakorn
2020.
Three-dimensional flip-flopping flow around a pair of dual-stepped circular cylinders in a side-by-side arrangement.
Physics of Fluids,
Vol. 32,
Issue. 12,
Zhang, Zhimeng
Ji, Chunning
Chen, Weilin
Hua, Yang
and
Srinil, Narakorn
2021.
Influence of boundary layer thickness and gap ratios on three-dimensional flow characteristics around a circular cylinder in proximity to a bottom plane.
Ocean Engineering,
Vol. 226,
Issue. ,
p.
108858.
Bai, X.
Ji, C.
Grant, P.
Phillips, N.
Oza, U.
Avital, E. J.
and
Williams, J. J. R.
2021.
Turbulent flow simulation of a single-blade Magnus rotor.
Advances in Aerodynamics,
Vol. 3,
Issue. 1,
Deng, Nan
Noack, Bernd R.
Morzyński, Marek
and
Pastur, Luc R.
2021.
Galerkin force model for transient and post-transient dynamics of the fluidic pinball.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 918,
Issue. ,
Deng, Nan
Pastur, Luc R.
Tuckerman, Laurette S.
and
Noack, Bernd R.
2021.
Coinciding local bifurcations in the Navier-Stokes equations.
EPL (Europhysics Letters),
Vol. 135,
Issue. 2,
p.
24002.
Blanchard, Antoine B.
Cornejo Maceda, Guy Y.
Fan, Dewei
Li, Yiqing
Zhou, Yu
Noack, Bernd R.
and
Sapsis, Themistoklis P.
2021.
Bayesian optimization for active flow control.
Acta Mechanica Sinica,
Vol. 37,
Issue. 12,
p.
1786.
Yan, Yuhao
Ji, Chunning
and
Srinil, Narakorn
2021.
On wake modulation and interaction features of a pair of dual-step circular cylinders in side-by-side arrangements.
Physics of Fluids,
Vol. 33,
Issue. 9,
Liu, Bin
2021.
A Nitsche stabilized finite element method: Application for heat and mass transfer and fluid–structure interaction.
Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering,
Vol. 386,
Issue. ,
p.
114101.
Freidooni, F.
Sohankar, A.
Rastan, M.R.
and
Shirani, E.
2021.
Flow field around two tandem non-identical-height square buildings via LES.
Building and Environment,
Vol. 201,
Issue. ,
p.
107985.
Cornejo Maceda, Guy Y.
Li, Yiqing
Lusseyran, François
Morzyński, Marek
and
Noack, Bernd R.
2021.
Stabilization of the fluidic pinball with gradient-enriched machine learning control.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 917,
Issue. ,
Zhu, Hongjun
Chu, Xin
Yan, Zhiyin
and
Gao, Yun
2021.
Coupling response of flow-induced oscillating cylinder with a pair of flow-induced rotating impellers.
Physics of Fluids,
Vol. 33,
Issue. 8,
Li, Yiqing
Cui, Wenshi
Jia, Qing
Li, Qiliang
Yang, Zhigang
Morzyński, Marek
and
Noack, Bernd R.
2022.
Explorative gradient method for active drag reduction of the fluidic pinball and slanted Ahmed body.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 932,
Issue. ,
Xu, Dong
Liu, Jia-ning
Wu, Yun-feng
and
Ji, Chun-ning
2022.
Numerical investigation of the dynamics of flexible vegetations in turbulent open-channel flows.
Journal of Hydrodynamics,
Vol. 34,
Issue. 4,
p.
681.
Duong, Viet Dung
Nguyen, Van Duc
Nguyen, Van Tien
and
Ngo, Ich Long
2022.
Low-Reynolds-number wake of three tandem elliptic cylinders.
Physics of Fluids,
Vol. 34,
Issue. 4,
Chen, Weilin
Ji, Chunning
Alam, Md. Mahbub
Xu, Dong
An, Hongwei
Tong, Feifei
and
Zhao, Yawei
2022.
Flow-induced vibrations of a D-section prism at a low Reynolds number.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 941,
Issue. ,
Zhang, Mohan
Yin, Bo
Guo, Dilong
Ji, Zhanling
and
Yang, Guowei
2022.
Numerical Study on the Flow Past Three Cylinders in Equilateral-Triangular Arrangement at Re = 3 × 106.
Applied Sciences,
Vol. 12,
Issue. 22,
p.
11835.
Lu, Jiaxing
Bi, Dianfang
Wang, Cong
Wei, Yingjie
Wang, Wenjun
and
Zhang, Dehua
2022.
Research on the interference characteristics of successively launched underwater projectiles.
Physics of Fluids,
Vol. 34,
Issue. 6,
Li, Feifan
Ji, Chunning
and
Xu, Dong
2022.
A novel optimization algorithm for the selective frequency damping parameters.
Physics of Fluids,
Vol. 34,
Issue. 12,
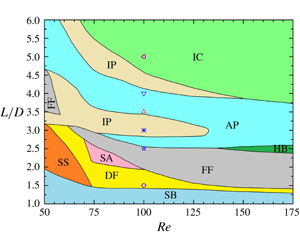
 $L/D(=1.0{-}6.0)$, Reynolds number
$L/D(=1.0{-}6.0)$, Reynolds number  $Re(=50{-}300)$ and three-dimensionality on the flow structures, hydrodynamic forces and Strouhal numbers, where
$Re(=50{-}300)$ and three-dimensionality on the flow structures, hydrodynamic forces and Strouhal numbers, where  $L$ is the cylinder centre-to-centre spacing and
$L$ is the cylinder centre-to-centre spacing and  $D$ is the cylinder diameter. The fluid dynamics involved is highly sensitive to both
$D$ is the cylinder diameter. The fluid dynamics involved is highly sensitive to both  $Re$ and
$Re$ and  $L/D$, leading to nine distinct flow structures, namely single bluff-body flow, deflected flow, flip-flopping flow, steady symmetric flow, steady asymmetric flow, hybrid flow, anti-phase flow, in-phase flow and fully developed in-phase co-shedding flow. The time-mean drag and lift of each cylinder are more sensitive to
$L/D$, leading to nine distinct flow structures, namely single bluff-body flow, deflected flow, flip-flopping flow, steady symmetric flow, steady asymmetric flow, hybrid flow, anti-phase flow, in-phase flow and fully developed in-phase co-shedding flow. The time-mean drag and lift of each cylinder are more sensitive to  $L/D$ than
$L/D$ than  $Re$ while fluctuating forces are less sensitive to
$Re$ while fluctuating forces are less sensitive to  $L/D$ than
$L/D$ than  $Re$. The three-dimensionality of the flow affects the development of the wake patterns, changing the
$Re$. The three-dimensionality of the flow affects the development of the wake patterns, changing the  $L/D$ ranges of different flow structures. A diagram of flow regimes, together with the contours of hydrodynamic forces, in the
$L/D$ ranges of different flow structures. A diagram of flow regimes, together with the contours of hydrodynamic forces, in the  $Re-L/D$ space, is given, providing physical insights into the complex interactions of the three cylinders.
$Re-L/D$ space, is given, providing physical insights into the complex interactions of the three cylinders.

