Crossref Citations
This article has been cited by the following publications. This list is generated based on data provided by
Crossref.
Alméras, E.
Plais, C.
Euzenat, F.
Risso, F.
Roig, V.
and
Augier, F.
2016.
Scalar mixing in bubbly flows: Experimental investigation and diffusivity modelling.
Chemical Engineering Science,
Vol. 140,
Issue. ,
p.
114.
Zamansky, R.
Coletti, F.
Massot, M.
and
Mani, A.
2016.
Turbulent thermal convection driven by heated inertial particles.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 809,
Issue. ,
p.
390.
Plais, Cécile
and
Augier, Frédéric
2016.
Effect of liquid viscosity on mixing times in bubble columns.
Theoretical Foundations of Chemical Engineering,
Vol. 50,
Issue. 6,
p.
969.
Alméras, Elise
Cazin, Sébastien
Roig, Véronique
Risso, Frédéric
Augier, Frédéric
and
Plais, Cécile
2016.
Time-resolved measurement of concentration fluctuations in a confined bubbly flow by LIF.
International Journal of Multiphase Flow,
Vol. 83,
Issue. ,
p.
153.
Ayeb Mrabtini, Hela
Bellakhal, Ghazi
and
Chahed, Jamel
2017.
Analysis of the homogeneous turbulence structure in uniformly sheared bubbly flow.
Nuclear Engineering and Design,
Vol. 320,
Issue. ,
p.
112.
Gvozdić, Biljana
Alméras, Elise
Mathai, Varghese
Zhu, Xiaojue
van Gils, Dennis P. M.
Verzicco, Roberto
Huisman, Sander G.
Sun, Chao
and
Lohse, Detlef
2018.
Experimental investigation of heat transport in homogeneous bubbly flow.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 845,
Issue. ,
p.
226.
Mathai, Varghese
Zhu, Xiaojue
Sun, Chao
and
Lohse, Detlef
2018.
Flutter to tumble transition of buoyant spheres triggered by rotational inertia changes.
Nature Communications,
Vol. 9,
Issue. 1,
Alméras, Elise
Plais, Cécile
Roig, Véronique
Risso, Frédéric
and
Augier, Frédéric
2018.
Mixing mechanisms in a low-sheared inhomogeneous bubble column.
Chemical Engineering Science,
Vol. 186,
Issue. ,
p.
52.
Kück, Ulf Daniel
Mießner, Ulrich
Aydin, Murat
and
Thöming, Jorg
2018.
Mixing time and mass transfer of rising bubbles in swarm turbulence.
Chemical Engineering Science,
Vol. 187,
Issue. ,
p.
367.
Mathai, Varghese
Huisman, Sander G.
Sun, Chao
Lohse, Detlef
and
Bourgoin, Mickaël
2018.
Dispersion of Air Bubbles in Isotropic Turbulence.
Physical Review Letters,
Vol. 121,
Issue. 5,
Risso, Frédéric
2018.
Agitation, Mixing, and Transfers Induced by Bubbles.
Annual Review of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 50,
Issue. 1,
p.
25.
Kong, G.
Buist, K.A.
Peters, E.A.J.F.
and
Kuipers, J.A.M.
2018.
Dual emission LIF technique for pH and concentration field measurement around a rising bubble.
Experimental Thermal and Fluid Science,
Vol. 93,
Issue. ,
p.
186.
Gemello, L.
Cappello, V.
Augier, F.
Marchisio, D.
and
Plais, C.
2018.
CFD-based scale-up of hydrodynamics and mixing in bubble columns.
Chemical Engineering Research and Design,
Vol. 136,
Issue. ,
p.
846.
Loisy, Aurore
Naso, Aurore
and
Spelt, Peter D. M.
2018.
The effective diffusivity of ordered and freely evolving bubbly suspensions.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 840,
Issue. ,
p.
215.
Alméras, Elise
Risso, Frédéric
Roig, Véronique
Plais, Cécile
and
Augier, Frédéric
2018.
Mixing mechanism in a two-dimensional bubble column.
Physical Review Fluids,
Vol. 3,
Issue. 7,
Gvozdić, Biljana
Dung, On-Yu
van Gils, Dennis P. M.
Bruggert, Gert-Wim H.
Alméras, Elise
Sun, Chao
Lohse, Detlef
and
Huisman, Sander G.
2019.
Twente mass and heat transfer water tunnel: Temperature controlled turbulent multiphase channel flow with heat and mass transfer.
Review of Scientific Instruments,
Vol. 90,
Issue. 7,
Gvozdić, Biljana
Dung, On-Yu
Alméras, Elise
van Gils, Dennis P.M.
Lohse, Detlef
Huisman, Sander G.
and
Sun, Chao
2019.
Experimental investigation of heat transport in inhomogeneous bubbly flow.
Chemical Engineering Science,
Vol. 198,
Issue. ,
p.
260.
Charton, Sophie
Couerbe, Grégory
and
Lamadie, Fabrice
2019.
Multiphase flow in small-gap geometry: A combined numerical and experimental study.
Progress in Nuclear Energy,
Vol. 112,
Issue. ,
p.
107.
Wang, Ziqi
Mathai, Varghese
and
Sun, Chao
2019.
Self-sustained biphasic catalytic particle turbulence.
Nature Communications,
Vol. 10,
Issue. 1,
Kalichetty, Srinivasa Sagar
Sundararajan, T.
and
Pattamatta, Arvind
2019.
Thermocapillary migration and interaction dynamics of droplets in a constricted domain.
Physics of Fluids,
Vol. 31,
Issue. 2,
 ${\it\alpha}$ ranging from 1 % to 13 %. The capture and transport of dye within bubble wakes is found to be negligible and the mixing turns out to result from the bubble-induced turbulence. It is described well by a regular diffusion process. The diffusion coefficient corresponding to the vertical direction is larger than that corresponding to the horizontal direction, owing to the larger intensity of the liquid fluctuations in the vertical direction. Two regimes of diffusion have been identified. At low gas volume fraction, the diffusion time scale is given by the correlation time of the bubble-induced turbulence and the diffusion coefficients increase roughly as
${\it\alpha}$ ranging from 1 % to 13 %. The capture and transport of dye within bubble wakes is found to be negligible and the mixing turns out to result from the bubble-induced turbulence. It is described well by a regular diffusion process. The diffusion coefficient corresponding to the vertical direction is larger than that corresponding to the horizontal direction, owing to the larger intensity of the liquid fluctuations in the vertical direction. Two regimes of diffusion have been identified. At low gas volume fraction, the diffusion time scale is given by the correlation time of the bubble-induced turbulence and the diffusion coefficients increase roughly as 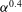 ${\it\alpha}^{0.4}$. At large gas volume fraction, the diffusion time scale is imposed by the time interval between two bubbles and the diffusion coefficients become almost independent of
${\it\alpha}^{0.4}$. At large gas volume fraction, the diffusion time scale is imposed by the time interval between two bubbles and the diffusion coefficients become almost independent of  ${\it\alpha}$. The transition between the two regimes occurs sooner in the horizontal direction (
${\it\alpha}$. The transition between the two regimes occurs sooner in the horizontal direction (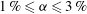 $1\,\%\leqslant {\it\alpha}\leqslant 3\,\%$) than in the vertical direction (
$1\,\%\leqslant {\it\alpha}\leqslant 3\,\%$) than in the vertical direction (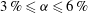 $3\,\%\leqslant {\it\alpha}\leqslant 6\,\%$). Physical models based on the hydrodynamic properties of the bubble swarm are introduced and guidelines for practical applications are suggested.
$3\,\%\leqslant {\it\alpha}\leqslant 6\,\%$). Physical models based on the hydrodynamic properties of the bubble swarm are introduced and guidelines for practical applications are suggested.


