Article contents
Dynamics of laser-induced cavitation bubbles near two perpendicular rigid walls
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 19 February 2018
Abstract
The behaviour of a laser-induced cavitation bubble near two perpendicular rigid walls and its dependence on the distance between bubble and walls is investigated experimentally. It was shown by means of high-speed photography with 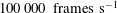 $100\,000~\text{frames}~\text{s}^{-1}$ that an inclined jet is formed during bubble collapse and the bubble migrates in the direction of the jet. At a given position of the bubble with respect to the horizontal wall, the inclination of the jet increases with decreasing distance between the bubble and the second, vertical wall. A bubble generated at equal distances from the walls develops a jet that is directed in their bisection. The penetration of the jet into the opposite bubble surface leads to the formation of an asymmetric toroidal bubble that is perpendicular to the jet direction. At a large distance from the rigid walls, the toroidal bubble collapses in the radial direction, eventually disintegrating into tiny microbubbles. When the bubble is in contact with the horizontal wall at its maximum expansion, the toroidal ring collapses in both radial and toroidal directions, starting from the bubble part opposite to the vertical wall, and the bubble achieves a crescent shape at the moment of second collapse. The bubble oscillation is accompanied by a strong migration along the horizontal wall.
$100\,000~\text{frames}~\text{s}^{-1}$ that an inclined jet is formed during bubble collapse and the bubble migrates in the direction of the jet. At a given position of the bubble with respect to the horizontal wall, the inclination of the jet increases with decreasing distance between the bubble and the second, vertical wall. A bubble generated at equal distances from the walls develops a jet that is directed in their bisection. The penetration of the jet into the opposite bubble surface leads to the formation of an asymmetric toroidal bubble that is perpendicular to the jet direction. At a large distance from the rigid walls, the toroidal bubble collapses in the radial direction, eventually disintegrating into tiny microbubbles. When the bubble is in contact with the horizontal wall at its maximum expansion, the toroidal ring collapses in both radial and toroidal directions, starting from the bubble part opposite to the vertical wall, and the bubble achieves a crescent shape at the moment of second collapse. The bubble oscillation is accompanied by a strong migration along the horizontal wall.
JFM classification
- Type
- JFM Papers
- Information
- Copyright
- © 2018 Cambridge University Press
References
Brujan et al. supplementary movie 1
Dynamics of a cavitation bubble situated near two perpendicular rigid walls for γh= 1.87, γv= 1.92, and Rmax= 0.83 mm. Side view
Brujan et al. supplementary movie 2
Dynamics of a cavitation bubble situated near two perpendicular rigid walls for γh= 1.11, γv= 15.25, and Rmax= 0.83 mm. Side view 2
Brujan et al. supplementary movie 3
Dynamics of a cavitation bubble situated near two perpendicular rigid walls for γh = 1.08, γv = 2.17, and Rmax = 0.85 mm. Side view
Brujan et al. supplementary movie 4
Dynamics of a cavitation bubble situated near two perpendicular rigid walls for γh= 1, γv = 16.8, and Rmax = 0.82 mm. Top view
Brujan et al. supplementary movie 5
Dynamics of a cavitation bubble situated near two perpendicular rigid walls for γh= 0.97, γv= 4.11, and Rmax = 0.73 mm. Top view
Brujan et al. supplementary movie 6
Dynamics of a cavitation bubble situated near two perpendicular rigid walls for γh = 1, γv = 2.59, and Rmax = 0.71 mm. Top view
- 103
- Cited by



