Crossref Citations
This article has been cited by the following publications. This list is generated based on data provided by
Crossref.
Yu, Rixin
Bai, Xue-Song
and
Bychkov, Vitaly
2015.
Fractal flame structure due to the hydrodynamic Darrieus-Landau instability.
Physical Review E,
Vol. 92,
Issue. 6,
Verma, Salman
and
Lipatnikov, Andrei N.
2016.
Does sensitivity of measured scaling exponents for turbulent burning velocity to flame configuration prove lack of generality of notion of turbulent burning velocity?.
Combustion and Flame,
Vol. 173,
Issue. ,
p.
77.
Elperin, T.
Kleeorin, N.
Liberman, M.
Lipatnikov, A. N.
Rogachevskii, I.
and
Yu, R.
2017.
Turbulent diffusion of chemically reacting flows: Theory and numerical simulations.
Physical Review E,
Vol. 96,
Issue. 5,
Zheng, Tianhang
You, Jiaping
and
Yang, Yue
2017.
Principal curvatures and area ratio of propagating surfaces in isotropic turbulence.
Physical Review Fluids,
Vol. 2,
Issue. 10,
Sabelnikov, Vladimir A.
and
Lipatnikov, Andrei N.
2017.
Recent Advances in Understanding of Thermal Expansion Effects in Premixed Turbulent Flames.
Annual Review of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 49,
Issue. 1,
p.
91.
Yu, Rixin
and
Lipatnikov, Andrei N.
2017.
DNS study of dependence of bulk consumption velocity in a constant-density reacting flow on turbulence and mixture characteristics.
Physics of Fluids,
Vol. 29,
Issue. 6,
Yu, Rixin
and
Lipatnikov, Andrei N.
2017.
Direct numerical simulation study of statistically stationary propagation of a reaction wave in homogeneous turbulence.
Physical Review E,
Vol. 95,
Issue. 6,
Lamioni, Rachele
Lapenna, Pasquale Eduardo
Troiani, Guido
and
Creta, Francesco
2018.
Flame Induced Flow Features in the Presence of Darrieus-Landau Instability.
Flow, Turbulence and Combustion,
Vol. 101,
Issue. 4,
p.
1137.
Nilsson, Thommie
Carlsson, Henning
Yu, Rixin
and
Bai, Xue-Song
2018.
Structures of turbulent premixed flames in the high Karlovitz number regime – DNS analysis.
Fuel,
Vol. 216,
Issue. ,
p.
627.
Lipatnikov, Andrei N.
2018.
Modeling and Simulation of Turbulent Combustion.
p.
181.
Lipatnikov, A. N.
Sabelnikov, V. A.
Chakraborty, N.
Nishiki, S.
and
Hasegawa, T.
2018.
A DNS Study of Closure Relations for Convection Flux Term in Transport Equation for Mean Reaction Rate in Turbulent Flow.
Flow, Turbulence and Combustion,
Vol. 100,
Issue. 1,
p.
75.
Lipatnikov, Andrei N.
Nishiki, Shinnosuke
and
Hasegawa, Tatsuya
2019.
Closure Relations for Fluxes of Flame Surface Density and Scalar Dissipation Rate in Turbulent Premixed Flames.
Fluids,
Vol. 4,
Issue. 1,
p.
43.
Yu, Rixin
and
Lipatnikov, Andrei N.
2019.
Surface-averaged quantities in turbulent reacting flows and relevant evolution equations.
Physical Review E,
Vol. 100,
Issue. 1,
Sabelnikov, V. A.
Yu, R.
and
Lipatnikov, A. N.
2019.
Thin reaction zones in constant-density turbulent flows at low Damköhler numbers: Theory and simulations.
Physics of Fluids,
Vol. 31,
Issue. 5,
Yu, Rixin
and
Lipatnikov, Andrei N.
2019.
A DNS Study of Sensitivity of Scaling Exponents for Premixed Turbulent Consumption Velocity to Transient Effects.
Flow, Turbulence and Combustion,
Vol. 102,
Issue. 3,
p.
679.
Yu, Rixin
Nillson, Thommie
Bai, Xue-Song
and
Lipatnikov, Andrei N.
2019.
Evolution of averaged local premixed flame thickness in a turbulent flow.
Combustion and Flame,
Vol. 207,
Issue. ,
p.
232.
Yu, Rixin
and
Lipatnikov, Andrei N.
2019.
DNS Study of the Bending Effect Due to Smoothing Mechanism.
Fluids,
Vol. 4,
Issue. 1,
p.
31.
Yu, Rixin
and
Lipatnikov, Andrei N.
2019.
Statistics conditioned to isoscalar surfaces in highly turbulent premixed reacting systems.
Computers & Fluids,
Vol. 187,
Issue. ,
p.
69.
Ahmed, Umair
Chakraborty, Nilanjan
and
Klein, Markus
2019.
Insights into the Bending Effect in Premixed Turbulent Combustion Using the Flame Surface Density Transport.
Combustion Science and Technology,
Vol. 191,
Issue. 5-6,
p.
898.
Sabelnikov, Vladimir A.
and
Lipatnikov, Andrei N.
2020.
A New Mathematical Framework for Describing Thin-Reaction-Zone Regime of Turbulent Reacting Flows at Low Damköhler Number.
Fluids,
Vol. 5,
Issue. 3,
p.
109.
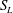 $S_{L}$ to the r.m.s. turbulent velocity
$S_{L}$ to the r.m.s. turbulent velocity 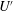 $U^{\prime }$ and various (50, 100 and 200) turbulent Reynolds numbers
$U^{\prime }$ and various (50, 100 and 200) turbulent Reynolds numbers 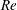 $\mathit{Re}$. By analysing computed data, the following issues were addressed: (i) dependence of the speed and thickness of the fully developed statistically planar mean front that envelops the interface on
$\mathit{Re}$. By analysing computed data, the following issues were addressed: (i) dependence of the speed and thickness of the fully developed statistically planar mean front that envelops the interface on  $U^{\prime }/S_{L}$ and
$U^{\prime }/S_{L}$ and  $\mathit{Re}$, (ii) dependence of the fully developed mean turbulent flux of a scalar
$\mathit{Re}$, (ii) dependence of the fully developed mean turbulent flux of a scalar  $c$ that characterizes the state of the fluid (
$c$ that characterizes the state of the fluid (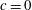 $c=0$ and 1 ahead and behind the interface respectively) on
$c=0$ and 1 ahead and behind the interface respectively) on 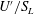 $U^{\prime }/S_{L}$ and
$U^{\prime }/S_{L}$ and 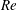 $\mathit{Re}$, (iii) evolution of the mean front speed, its thickness, and the mean scalar flux during the front development after embedding a planar interface into the forced turbulence and (iv) relation between canonical and conditioned moments of the velocity, velocity gradient and pressure gradient fields.
$\mathit{Re}$, (iii) evolution of the mean front speed, its thickness, and the mean scalar flux during the front development after embedding a planar interface into the forced turbulence and (iv) relation between canonical and conditioned moments of the velocity, velocity gradient and pressure gradient fields.


