Article contents
Direct numerical simulation of turbulence in injection-driven three-dimensional cylindrical flows
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 19 January 2011
Abstract
Incompressible turbulent flow in a periodic circular pipe with strong injection is studied as a simplified model for the core flow in a solid-propellant rocket motor and other injection-driven internal flows. The model is based on a multi-scale asymptotic approach. The intended application of the current study is erosive burning of solid propellants. Relevant analysis for easily accessible parameters for this application, such as the magnitudes, main frequencies and wavelengths associated with the near-wall shear, and the assessment of near-wall turbulence viscosity is focused on. It is found that, unlike flows with weak or no injection, the near-wall shear is dominated by the root mean square of the streamwise velocity which is a function of the Reynolds number, while the mean streamwise velocity is only weakly dependent on the Reynolds number. As a result, a new wall-friction velocity 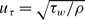 , based on the shear stress derived from the sum of the mean and the root mean square, i.e.
, based on the shear stress derived from the sum of the mean and the root mean square, i.e. 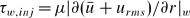 , is proposed for the scaling of turbulent viscosity for turbulent flows with strong injection. We also show that the mean streamwise velocity profile has an inflection point near the injecting surface.
, is proposed for the scaling of turbulent viscosity for turbulent flows with strong injection. We also show that the mean streamwise velocity profile has an inflection point near the injecting surface.
JFM classification
- Type
- Papers
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Cambridge University Press 2011
References
REFERENCES
- 4
- Cited by


