Article contents
Explicit results on conditional distributions of generalized exponential mixtures
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 04 September 2020
Abstract
For independent exponentially distributed random variables 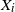 $X_i$
,
$X_i$
, 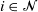 $i\in {\mathcal{N}}$
, with distinct rates
$i\in {\mathcal{N}}$
, with distinct rates 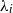 ${\lambda}_i$
we consider sums
${\lambda}_i$
we consider sums 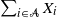 $\sum_{i\in\mathcal{A}} X_i$
for
$\sum_{i\in\mathcal{A}} X_i$
for 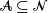 $\mathcal{A}\subseteq {\mathcal{N}}$
which follow generalized exponential mixture distributions. We provide novel explicit results on the conditional distribution of the total sum
$\mathcal{A}\subseteq {\mathcal{N}}$
which follow generalized exponential mixture distributions. We provide novel explicit results on the conditional distribution of the total sum 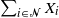 $\sum_{i\in {\mathcal{N}}}X_i$
given that a subset sum
$\sum_{i\in {\mathcal{N}}}X_i$
given that a subset sum 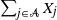 $\sum_{j\in \mathcal{A}}X_j$
exceeds a certain threshold value
$\sum_{j\in \mathcal{A}}X_j$
exceeds a certain threshold value 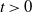 $t>0$
, and vice versa. Moreover, we investigate the characteristic tail behavior of these conditional distributions for
$t>0$
, and vice versa. Moreover, we investigate the characteristic tail behavior of these conditional distributions for 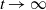 $t\to\infty$
. Finally, we illustrate how our probabilistic results can be applied in practice by providing examples from both reliability theory and risk management.
$t\to\infty$
. Finally, we illustrate how our probabilistic results can be applied in practice by providing examples from both reliability theory and risk management.
Keywords
- Type
- Research Papers
- Information
- Copyright
- © Applied Probability Trust 2020
References
- 7
- Cited by



