No CrossRef data available.
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 12 April 2016
The paper presents the results of the orbit determination of geosynchronous satellites derived from 1921 positional observations of a few dozens of satellites obtained at the double wide-angle astrograph DWA (D=0.4m, F=2m) of the Main Astronomical Observatory of the National Academy of Sciences of Ukraine in 1985–1991. The observations cover the longitude range from 19° W to 80° E. Orbital inclination of the observed objects is less than 3°. The mean values of the rms residuals are 0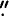 66 in R.A. and 1
66 in R.A. and 1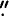 01 in Dec. over all processed orbital arcs.
01 in Dec. over all processed orbital arcs.