No CrossRef data available.
Article contents
The Evolution of the Precursor of SN 1987 A
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 12 April 2016
Summary
Ideally, the evolutionary models for the precursor of SN 1987 A should account for both the SN properties and the observational constraints for massive stars with relevant mass and composition.
Mass loss is an essential property of massive star evolution. Recent parametrisations of mass loss rates 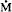 for galactic stars cover the whole HR diagram. There are indications that for given L and Teff values,
for galactic stars cover the whole HR diagram. There are indications that for given L and Teff values, 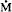 is lower at lower metallicity and therefore
is lower at lower metallicity and therefore 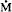 is lower in the LMC than in the Galaxy, thus we take
is lower in the LMC than in the Galaxy, thus we take 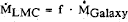 with f < 1. Various models of an intitial 20 M⊙ star with f=0.2, 0.4, 0.6 and 1.0 are constructed (cf. Fig. 1) with a metallicity Z=0.006 and a moderate overshooting dover=0.3 Hp. From these models, we suggest an initial mass on the zero age sequence of 17 to 18 M⊙. The pre-SN location in the HR diagram very much depends on the remaining stellar mass, or more precisely on the mass of the remaining H-rich envelope. A final location at log Teff ≃ 4.2 is obtained for a final mass of about 9.0 M⊙ (cf. Fig.1). Scaled to an initial value of 17 M⊙, this corresponds to a final mass of about 8 M⊙ and a remaining H-rich envelope of a few tenths of a solar mass at most. The stellar surface exhibits CNO equilibrium values with C/N ≃ 0.01 and O/N ≃ 0.1 in mass fraction, and an hydrogen content X (surf) = 0.39. The blue progenitor is obtained for f=0.4, i.e. for
with f < 1. Various models of an intitial 20 M⊙ star with f=0.2, 0.4, 0.6 and 1.0 are constructed (cf. Fig. 1) with a metallicity Z=0.006 and a moderate overshooting dover=0.3 Hp. From these models, we suggest an initial mass on the zero age sequence of 17 to 18 M⊙. The pre-SN location in the HR diagram very much depends on the remaining stellar mass, or more precisely on the mass of the remaining H-rich envelope. A final location at log Teff ≃ 4.2 is obtained for a final mass of about 9.0 M⊙ (cf. Fig.1). Scaled to an initial value of 17 M⊙, this corresponds to a final mass of about 8 M⊙ and a remaining H-rich envelope of a few tenths of a solar mass at most. The stellar surface exhibits CNO equilibrium values with C/N ≃ 0.01 and O/N ≃ 0.1 in mass fraction, and an hydrogen content X (surf) = 0.39. The blue progenitor is obtained for f=0.4, i.e. for 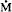 -values in the LMC equal to 40% of the galactic values.
-values in the LMC equal to 40% of the galactic values.
- Type
- Part III. Chemical and Dynamical Structures of Exploding Stars
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Springer-Verlag 1988


