No CrossRef data available.
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 30 March 2016
The MERIT programme of international collaboration to monitor earth-rotation and to intercompare the techniques of observation and analysis has fostered the development of the use of space techniques. Earth-rotation parameters are now determined regularly with a precision that is better than 1 milliarcsecond (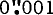 ) and the relative positions of the observing stations are determined to better than 1 decimetre (0.1 m). It is therefore necessary that the terrestrial and celestial reference frames be defined more precisely. The MERIT and COTES Working Groups have proposed that new conventional terrestrial and celestial reference systems be established and that the maintenance of these systems be the responsibility of a new International Earth Rotation Service. The new reference frames are to be based on the adoption of positions and motions of designated stations and extragalactic radio sources. Appropriate models and parameters will be associated with these frames to form reference systems so that observations can be used to determine the rotation of the terrestrial frame with respect to the celestial frame.
) and the relative positions of the observing stations are determined to better than 1 decimetre (0.1 m). It is therefore necessary that the terrestrial and celestial reference frames be defined more precisely. The MERIT and COTES Working Groups have proposed that new conventional terrestrial and celestial reference systems be established and that the maintenance of these systems be the responsibility of a new International Earth Rotation Service. The new reference frames are to be based on the adoption of positions and motions of designated stations and extragalactic radio sources. Appropriate models and parameters will be associated with these frames to form reference systems so that observations can be used to determine the rotation of the terrestrial frame with respect to the celestial frame.