Article contents
STRONG APPROXIMATION THEOREM FOR ABSOLUTELY IRREDUCIBLE VARIETIES OVER THE COMPOSITUM OF ALL SYMMETRIC EXTENSIONS OF A GLOBAL FIELD
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 13 July 2018
Abstract
Let K be a global field, 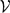 $\mathcal{V}$ a proper subset of the set of all primes of K,
$\mathcal{V}$ a proper subset of the set of all primes of K, 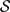 $\mathcal{S}$ a finite subset of
$\mathcal{S}$ a finite subset of 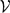 $\mathcal{V}$, and
$\mathcal{V}$, and 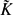 ${\tilde K}$ (resp. Ksep) a fixed algebraic (resp. separable algebraic) closure of K with
${\tilde K}$ (resp. Ksep) a fixed algebraic (resp. separable algebraic) closure of K with 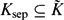 $K_\mathrm{sep}\{\subseteq}{\tilde K}$. Let Gal(K) = Gal(Ksep/K) be the absolute Galois group of K. For each
$K_\mathrm{sep}\{\subseteq}{\tilde K}$. Let Gal(K) = Gal(Ksep/K) be the absolute Galois group of K. For each 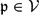 $\mathfrak{p}\in\mathcal{V}$, we choose a Henselian (respectively, a real or algebraic) closure
$\mathfrak{p}\in\mathcal{V}$, we choose a Henselian (respectively, a real or algebraic) closure 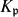 $K_\mathfrak{p}$ of K at
$K_\mathfrak{p}$ of K at 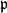 $\mathfrak{p}$ in
$\mathfrak{p}$ in 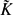 ${\tilde K}$ if
${\tilde K}$ if 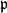 $\mathfrak{p}$ is non-archimedean (respectively, archimedean). Then,
$\mathfrak{p}$ is non-archimedean (respectively, archimedean). Then, 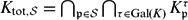 $K_{\mathrm{tot},\mathcal{S}}=\bigcap_{\mathfrak{p}\in\mathcal{S}}\bigcap_{\tau\in{\rm Gal}(K)}K_\mathfrak{p}^\tau$ is the maximal Galois extension of K in Ksep in which each
$K_{\mathrm{tot},\mathcal{S}}=\bigcap_{\mathfrak{p}\in\mathcal{S}}\bigcap_{\tau\in{\rm Gal}(K)}K_\mathfrak{p}^\tau$ is the maximal Galois extension of K in Ksep in which each 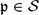 $\mathfrak{p}\in\mathcal{S}$ totally splits. For each
$\mathfrak{p}\in\mathcal{S}$ totally splits. For each 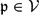 $\mathfrak{p}\in\mathcal{V}$, we choose a
$\mathfrak{p}\in\mathcal{V}$, we choose a 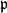 $\mathfrak{p}$-adic absolute value
$\mathfrak{p}$-adic absolute value 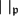 $|~|_\mathfrak{p}$ of
$|~|_\mathfrak{p}$ of 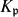 $K_\mathfrak{p}$ and extend it in the unique possible way to
$K_\mathfrak{p}$ and extend it in the unique possible way to 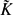 ${\tilde K}$. Finally, we denote the compositum of all symmetric extensions of K by Ksymm. We consider an affine absolutely integral variety V in
${\tilde K}$. Finally, we denote the compositum of all symmetric extensions of K by Ksymm. We consider an affine absolutely integral variety V in 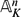 $\mathbb{A}_K^n$. Suppose that for each
$\mathbb{A}_K^n$. Suppose that for each 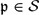 $\mathfrak{p}\in\mathcal{S}$ there exists a simple
$\mathfrak{p}\in\mathcal{S}$ there exists a simple 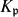 $K_\mathfrak{p}$-rational point
$K_\mathfrak{p}$-rational point 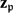 $\mathbf{z}_\mathfrak{p}$ of V and for each
$\mathbf{z}_\mathfrak{p}$ of V and for each 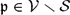 $\mathfrak{p}\in\mathcal{V}\smallsetminus\mathcal{S}$ there exists
$\mathfrak{p}\in\mathcal{V}\smallsetminus\mathcal{S}$ there exists  $\mathbf{z}_\mathfrak{p}\in V({\tilde K})$ such that in both cases
$\mathbf{z}_\mathfrak{p}\in V({\tilde K})$ such that in both cases 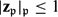 $|\mathbf{z}_\mathfrak{p}|_\mathfrak{p}\le1$ if
$|\mathbf{z}_\mathfrak{p}|_\mathfrak{p}\le1$ if 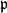 $\mathfrak{p}$ is non-archimedean and
$\mathfrak{p}$ is non-archimedean and 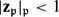 $|\mathbf{z}_\mathfrak{p}|_\mathfrak{p}<1$ if
$|\mathbf{z}_\mathfrak{p}|_\mathfrak{p}<1$ if 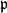 $\mathfrak{p}$ is archimedean. Then, there exists
$\mathfrak{p}$ is archimedean. Then, there exists 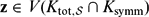 $\mathbf{z}\in V(K_{\mathrm{tot},\mathcal{S}}\cap K_\mathrm{symm})$ such that for all
$\mathbf{z}\in V(K_{\mathrm{tot},\mathcal{S}}\cap K_\mathrm{symm})$ such that for all 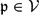 $\mathfrak{p}\in\mathcal{V}$ and for all τ ∈ Gal(K), we have
$\mathfrak{p}\in\mathcal{V}$ and for all τ ∈ Gal(K), we have 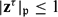 $|\mathbf{z}^\tau|_\mathfrak{p}\le1$ if
$|\mathbf{z}^\tau|_\mathfrak{p}\le1$ if 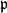 $\mathfrak{p}$ is archimedean and
$\mathfrak{p}$ is archimedean and 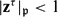 $|\mathbf{z}^\tau|_\mathfrak{p}<1$ if
$|\mathbf{z}^\tau|_\mathfrak{p}<1$ if 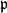 $\mathfrak{p}$ is non-archimedean. For
$\mathfrak{p}$ is non-archimedean. For 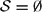 $\mathcal{S}=\emptyset$, we get as a corollary that the ring of integers of Ksymm is Hilbertian and Bezout.
$\mathcal{S}=\emptyset$, we get as a corollary that the ring of integers of Ksymm is Hilbertian and Bezout.
MSC classification
- Type
- Research Article
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Glasgow Mathematical Journal Trust 2018
References
REFERENCES
- 2
- Cited by


