No CrossRef data available.
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 13 May 2020
Erdös and Zaremba showed that 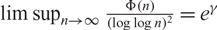 $ \limsup_{n\to \infty} \frac{\Phi(n)}{(\log\log n)^2}=e^\gamma$
, γ being Euler’s constant, where
$ \limsup_{n\to \infty} \frac{\Phi(n)}{(\log\log n)^2}=e^\gamma$
, γ being Euler’s constant, where  $\Phi(n)=\sum_{d|n} \frac{\log d}{d}$
.
$\Phi(n)=\sum_{d|n} \frac{\log d}{d}$
.
We extend this result to the function 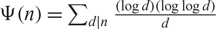 $\Psi(n)= \sum_{d|n} \frac{(\log d )(\log\log d)}{d}$
and some other functions. We show that
$\Psi(n)= \sum_{d|n} \frac{(\log d )(\log\log d)}{d}$
and some other functions. We show that 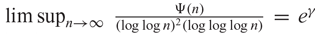 $ \limsup_{n\to \infty}\, \frac{\Psi(n)}{(\log\log n)^2(\log\log\log n)}\,=\, e^\gamma$
. The proof requires a new approach. As an application, we prove that for any
$ \limsup_{n\to \infty}\, \frac{\Psi(n)}{(\log\log n)^2(\log\log\log n)}\,=\, e^\gamma$
. The proof requires a new approach. As an application, we prove that for any 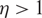 $\eta>1$
, any finite sequence of reals
$\eta>1$
, any finite sequence of reals 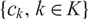 $\{c_k, k\in K\}$
,
$\{c_k, k\in K\}$
, 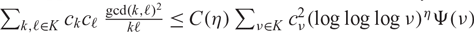 $\sum_{k,\ell\in K} c_kc_\ell \, \frac{\gcd(k,\ell)^{2}}{k\ell} \le C(\eta) \sum_{\nu\in K} c_\nu^2(\log\log\log \nu)^\eta \Psi(\nu)$
, where C(η) depends on η only. This improves a recent result obtained by the author.
$\sum_{k,\ell\in K} c_kc_\ell \, \frac{\gcd(k,\ell)^{2}}{k\ell} \le C(\eta) \sum_{\nu\in K} c_\nu^2(\log\log\log \nu)^\eta \Psi(\nu)$
, where C(η) depends on η only. This improves a recent result obtained by the author.