Article contents
YANG–BAXTER FIELD FOR SPIN HALL–LITTLEWOOD SYMMETRIC FUNCTIONS
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 31 October 2019
Abstract
Employing bijectivization of summation identities, we introduce local stochastic moves based on the Yang–Baxter equation for 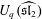 $U_{q}(\widehat{\mathfrak{sl}_{2}})$. Combining these moves leads to a new object which we call the spin Hall–Littlewood Yang–Baxter field—a probability distribution on two-dimensional arrays of particle configurations on the discrete line. We identify joint distributions along down-right paths in the Yang–Baxter field with spin Hall–Littlewood processes, a generalization of Schur processes. We consider various degenerations of the Yang–Baxter field leading to new dynamic versions of the stochastic six-vertex model and of the Asymmetric Simple Exclusion Process.
$U_{q}(\widehat{\mathfrak{sl}_{2}})$. Combining these moves leads to a new object which we call the spin Hall–Littlewood Yang–Baxter field—a probability distribution on two-dimensional arrays of particle configurations on the discrete line. We identify joint distributions along down-right paths in the Yang–Baxter field with spin Hall–Littlewood processes, a generalization of Schur processes. We consider various degenerations of the Yang–Baxter field leading to new dynamic versions of the stochastic six-vertex model and of the Asymmetric Simple Exclusion Process.
- Type
- Research Article
- Information
- Creative Commons
- This is an Open Access article, distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution licence (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted re-use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
- Copyright
- © The Author(s) 2019
References
- 14
- Cited by


