No CrossRef data available.
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 13 August 2019
Answering a longstanding problem originating in Christensen’s seminal work on Haar null sets [Math. Scand. 28 (1971), 124–128; Israel J. Math. 13 (1972), 255–260; Topology and Borel Structure. Descriptive Topology and Set Theory with Applications to Functional Analysis and Measure Theory, North-Holland Mathematics Studies, 10 (Notas de Matematica, No. 51). (North-Holland Publishing Co., Amsterdam–London; American Elsevier Publishing Co., Inc., New York, 1974), iii+133 pp], we show that a universally measurable homomorphism between Polish groups is automatically continuous. Using our general analysis of continuity of group homomorphisms, this result is used to calibrate the strength of the existence of a discontinuous homomorphism between Polish groups. In particular, it is shown that, modulo 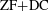 $\text{ZF}+\text{DC}$, the existence of a discontinuous homomorphism between Polish groups implies that the Hamming graph on
$\text{ZF}+\text{DC}$, the existence of a discontinuous homomorphism between Polish groups implies that the Hamming graph on 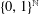 $\{0,1\}^{\mathbb{N}}$ has finite chromatic number.
$\{0,1\}^{\mathbb{N}}$ has finite chromatic number.