No CrossRef data available.
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 17 April 2020
Participation in social, cultural, and physical activities positively influences perceptions of health and quality of life. Few have studied how substance abuse influences patients’ participation in social, cultural and physical activities.
We examined patterns of past, recent and future (desired) activities of patients being admitted to substance abuse treatment at a Norwegian university hospital.
A questionnaire was developed specifically for the self-reporting of social, cultural, and physical activities. Psychiatric diagnoses including substance use diagnoses and other clinical and demographic data were also obtained. Data were analysed with descriptive and comparative analyses, including ANOVA.
78 patients responded (71%), 23 women, 55 men. Mean age was 38. 71% had a diagnosis of mental and behavioural disorders due to psychoactive substance use, while some had personality disorders (8.9%) or schizophrenia (3.6%). The total amount of activities had dropped significantly compared to before the respondents started abusing substances, and the drop was particularly pronounced for physical activities (Figure).
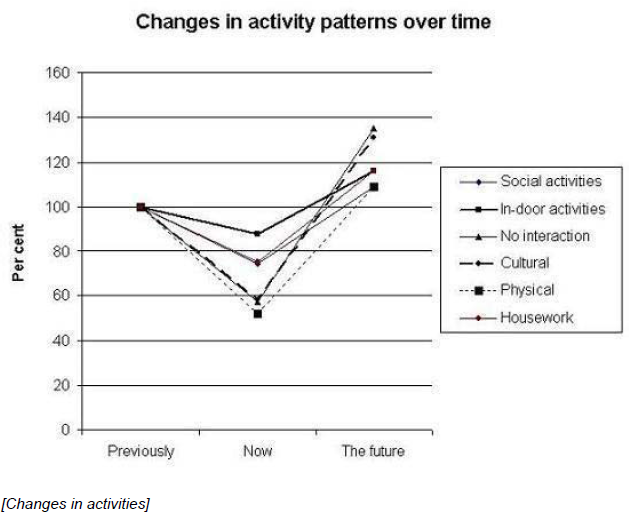
Most expressed an interest in increasing their social, cultural, and physical activities.
The total amount of social, cultural, and physical activities falls markedly after starting substance abuse. Helping patients regain positive activities may improve subjective health and quality of life.
Comments
No Comments have been published for this article.