Fig. 1
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 16 April 2020
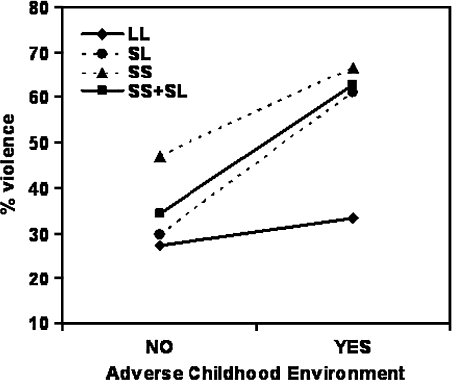
We investigated the contribution of polymorphisms shown to moderate transcription of serotonin transporter (5HTT) and monoamine oxidase A (MAOA) to the development of violence, and furthermore to test for gene x environment interactions. To do so, a cohort of 184 adult male volunteers referred for forensic assessment were assigned to a violent or non-violent group. 45% of violent, but only 30% of non-violent individuals carried the low-activity, short MAOA allele. In the violent group, carriers of low-function variants of 5HTT were found in 77%, as compared to 59%. Logistic regression was performed and the best fitting model revealed a significant, independent effect of childhood environment and MAOA genotype. A significant influence of an interaction between childhood environment and 5HTT genotype was found (Fig. 1). MAOA thus appears to be independently associated with violent crime, while there is a relevant 5HTT x environment interaction.

Fig. 1

Fig. 1
Comments
No Comments have been published for this article.