No CrossRef data available.
Article contents
Is there a dose-response relationship between cannabis use and violence? A longitudinal study in individuals with severe mental disorders
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 19 July 2023
Abstract
Recent longitudinal studies point towards the existence of a positive relationship between cannabis use and violence in people with severe mental disorders. However, the existence of a dose-response relationship between the frequency and/or the severity of cannabis use and violence has seldom been investigated.
This study aimed to determine if a dose-response relationship between cannabis use and violence exists in a psychiatric population.
This observational study was conducted at the Institut universitaire de santé mentale de Montréal (Montréal, Canada). A total of 98 outpatients (81 males and 17 females, all over 18 years of age) with severe mental disorders were included in the analyses. Clinical evaluations were conducted every 3 months for a year. Substance use, violent behaviors, and potential covariables were assessed through self-reported assessments, urinary testing, as well as clinical, criminal, and police records. Using generalized estimating equations, the association between cannabis use frequency (non-users, occasional, regular, and frequent users, assessed using the Time-Line Follow-Back and confirmed with urinary testing) and violence was investigated, as well as the association between the severity of cannabis use (measured using the Cannabis Use Problems Identification Test – CUPIT) and violent behaviors.
Cannabis use frequency and severity were significant predictors of violent behaviors. After adjustment for time, age, sex, ethnicity, psychiatric diagnoses, impulsivity and use of alcohol and stimulants, odds ratios were of 1.91 (p <0.001) between each frequency profile, and 1.040 (p <0.001) for each increase of one point of the severity of cannabis use score (0 to 79).
Image:
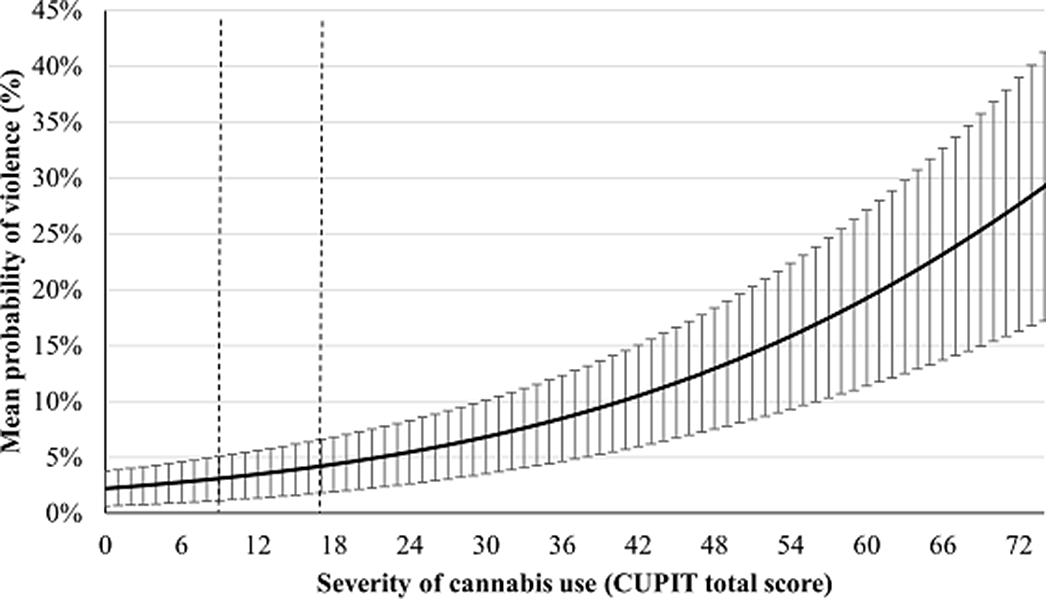
These findings have important implications for clinicians, demonstrating that cannabis use may have serious adverse consequences in a psychiatric population. Nevertheless, the mechanisms underlying this association remain unclear.
None Declared
- Type
- Abstract
- Information
- European Psychiatry , Volume 66 , Special Issue S1: Abstracts of the 31st European Congress of Psychiatry , March 2023 , pp. S135 - S136
- Creative Commons
- This is an Open Access article, distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution licence (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted re-use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
- Copyright
- © The Author(s), 2023. Published by Cambridge University Press on behalf of the European Psychiatric Association



Comments
No Comments have been published for this article.