No CrossRef data available.
Article contents
Dynamic time warp analysis of individual symptom trajectories in patients with bipolar disorder
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 19 July 2023
Abstract
Manic and depressive mood states in bipolar disorder (BD) may emerge from the non-linear relations between constantly changing mood symptoms exhibited as a complex dynamic system. Dynamic Time Warp (DTW) is an algorithm that may capture symptom interactions from panel data with sparse observations over time.
The current study is the first to analyze a time series of depression and manic symptoms using DTW analyses in patients with BD. We studied interactions and relative changes in symptom severity within and between participants.
The Young Mania Rating Scale and Quick Inventory of Depressive Symptomatology were repeatedly assessed in 141 patients with BD, with on average 5.5 assessments per patient every 3 to 6 months. DTW calculated the distance between each of the 27*27 pairs of standardized symptom scores. The changing profile of standardized symptom scores of BD patients was analyzed in individual patients, yielding symptom dimensions in aggregated group-level analyses. Using an asymmetric time-window, symptom changes that preceded other symptom changes (i.e., Granger causality) yielded a directed network.
The mean age of the patients was 40.1 (SD 13.5) years old, and 60% were female. Idiographic symptom networks were highly variable between patients. Yet, nomothetic analyses showed five symptom dimensions: core (hypo)mania (6 items), dysphoric mania (5 items), lethargy (7 items), somatic/suicidality (6 items), and sleep (3 items). Symptoms of the ‘Lethargy’ dimension showed the highest out-strength, and its changes preceded those of ‘somatic/suicidality’, while changes in ‘core (hypo)mania’ preceded those of ‘dysphoric mania’.
Image:
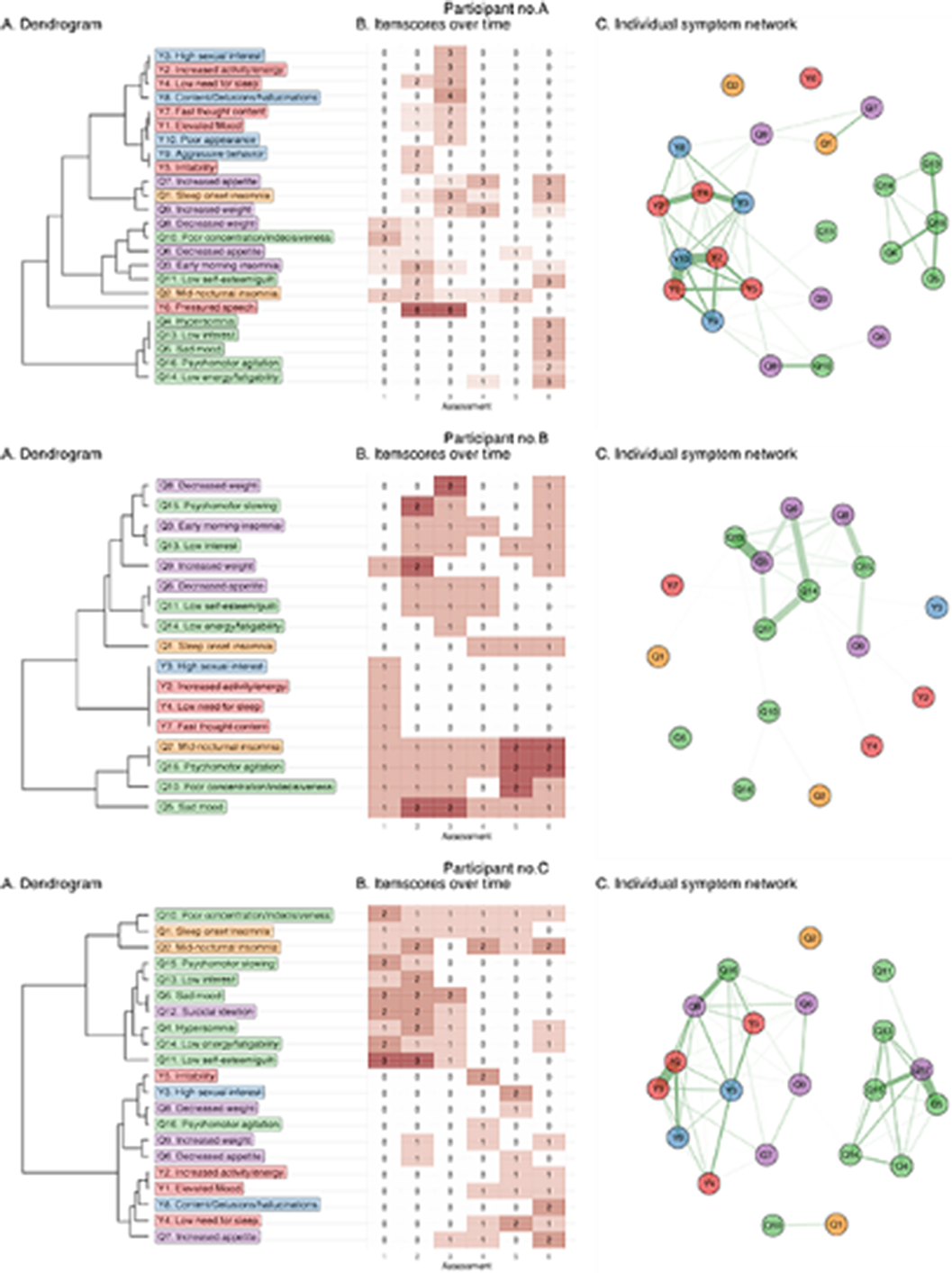
Image 2:
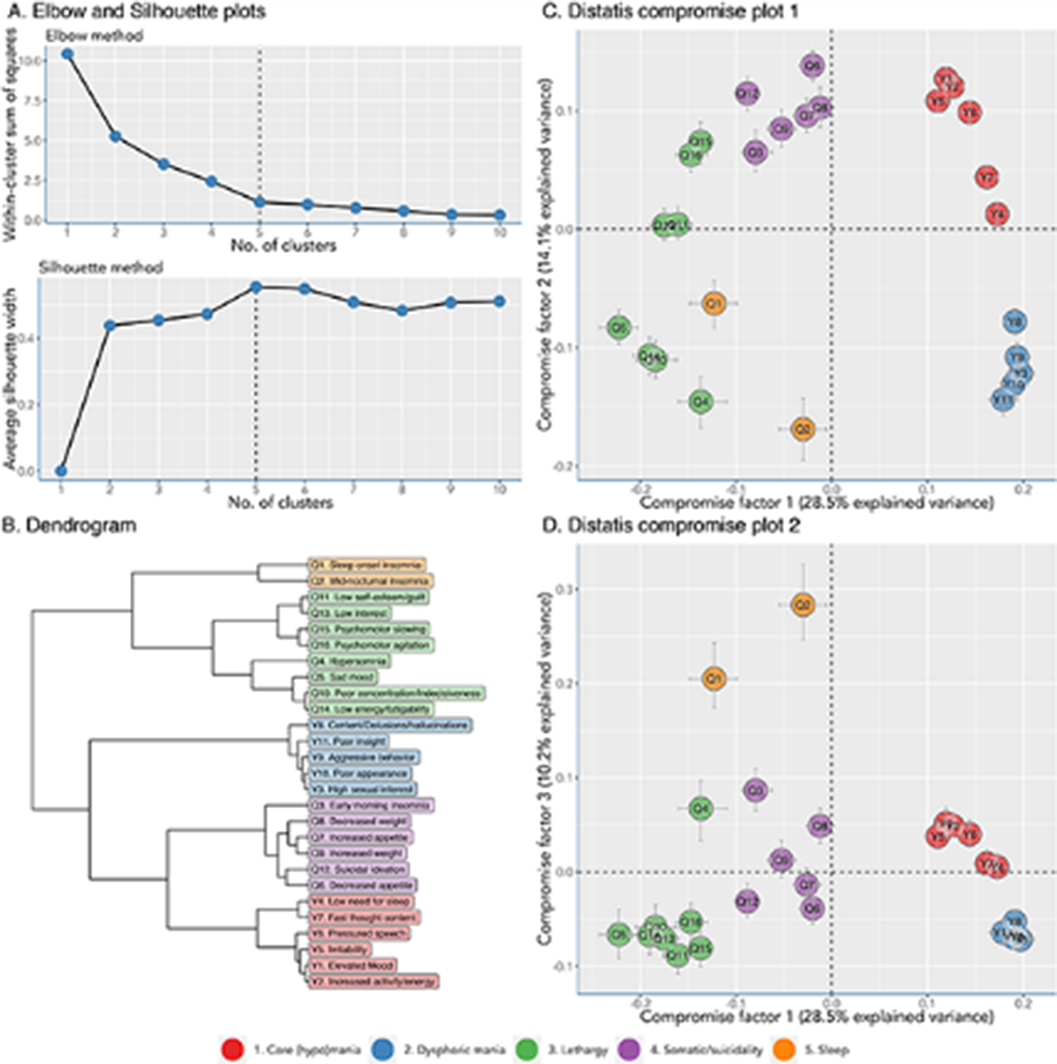
Image 3:
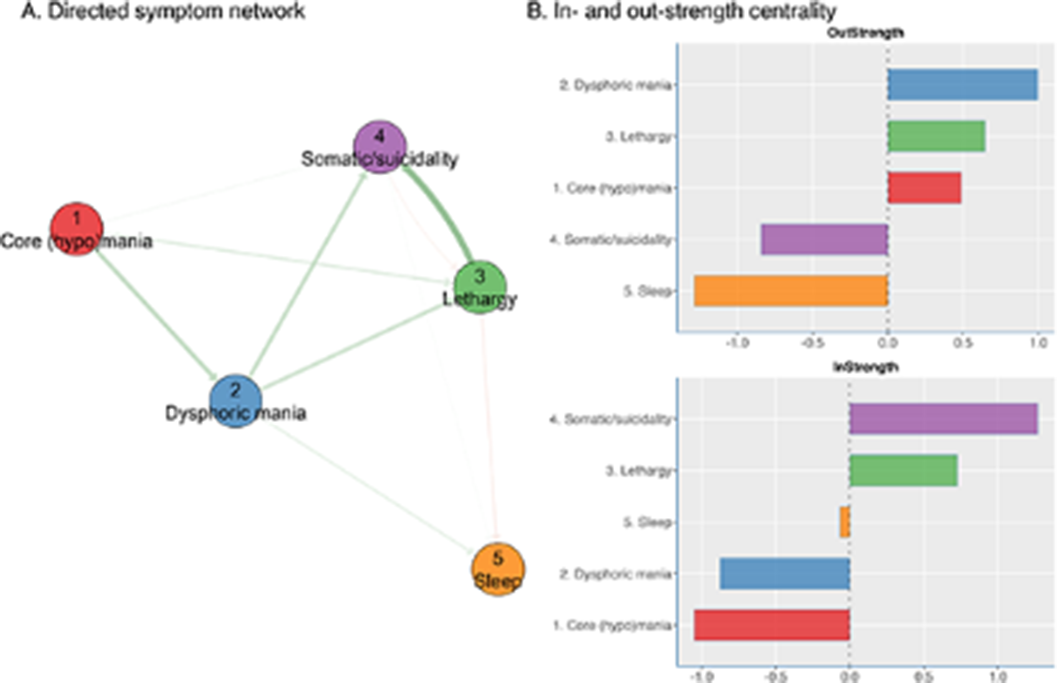
DTW may help to capture meaningful BD symptom interactions from panel data with sparse observations. It may increase insight into the temporal dynamics of symptoms, as those with high out-strength (rather than high in-strength) could be promising targets for intervention.
None Declared
- Type
- Abstract
- Information
- European Psychiatry , Volume 66 , Special Issue S1: Abstracts of the 31st European Congress of Psychiatry , March 2023 , pp. S578 - S579
- Creative Commons
- This is an Open Access article, distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution licence (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted re-use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
- Copyright
- © The Author(s), 2023. Published by Cambridge University Press on behalf of the European Psychiatric Association



Comments
No Comments have been published for this article.