No CrossRef data available.
Article contents
Modelling the pharmacodynamic interaction between remifentanil and propofol by EEG-controlled dosing
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 30 June 2005
Extract
Summary
Background and objective: Knowledge of the pharmacodynamic interaction between remifentanil and propofol is important to permit optimal dosage strategies. We studied this pharmacodynamic interaction using the median power frequency of the processed electroencephalogram as a control parameter for feedback-controlled dosing of propofol.
Methods: Twenty-one patients were given total intravenous anaesthesia with remifentanil and propofol. During three target-controlled infusion regimens, the target concentrations of remifentanil (5, 10, 15 ng mL−1) and propofol dosing were automatically adjusted to keep the median power frequency in the range 2 ± 0.5 Hz. In each patient and during each remifentanil target concentration, four arterial propofol/remifentanil concentration pairs were measured. The type of interaction was tested using the relative distance from the line of additivity and the isobole was modelled using Bernstein splines.
Results: The results from 13 patients were used for data analysis. The measured remifentanil concentrations during the three targets were (mean ± SD): 3.6 ± 0.9, 8.1 ± 2.5 and 12.4 ± 2.8 ng mL−1. The corresponding propofol concentrations were 2.64 ± 0.86, 2.13 ± 0.58 and 2.09 ± 0.58 μg mL−1. The data were best described with an additive type of interaction and the isobole was estimated using:
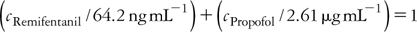
Conclusions: Within the studied concentration range, remifentanil and propofol showed an additive type of pharmacodynamic interaction on the electroencephalogram.
Keywords
- Type
- Original Article
- Information
- Copyright
- 2003 European Society of Anaesthesiology


