Article contents
Polynomial deviation bounds for recurrent Harris processeshaving general state space
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 08 February 2013
Abstract
Consider a strong Markov process in continuous time, taking values in some Polish statespace. Recently, Douc et al. [Stoc. Proc. Appl.119, (2009) 897–923] introduced verifiable conditions in terms ofa supermartingale property implying an explicit control of modulated moments of hittingtimes. We show how this control can be translated into a control of polynomial moments ofabstract regeneration times which are obtained by using the regeneration method ofNummelin, extended to the time-continuous context. As a consequence, if ap-th moment of the regeneration times exists, we obtain non asymptoticdeviation bounds of the form 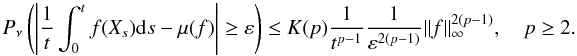 Pν1t∫0tf(Xs)ds−μ(f)≥ε≤K(p)1tp−11ε2(p−1)∥f∥∞2(p−1), p≥2.
Pν1t∫0tf(Xs)ds−μ(f)≥ε≤K(p)1tp−11ε2(p−1)∥f∥∞2(p−1), p≥2.
Keywords
- Type
- Research Article
- Information
- Copyright
- © EDP Sciences, SMAI, 2013
References
- 3
- Cited by


