No CrossRef data available.
Article contents
On uniform distribution of polynomials and good universality
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 10 August 2018
Abstract
Suppose  $(k_{n})_{n\geq 1}$ is Hartman uniformly distributed and good universal. Also suppose
$(k_{n})_{n\geq 1}$ is Hartman uniformly distributed and good universal. Also suppose 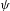 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D713}$ is a polynomial with at least one coefficient other than
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D713}$ is a polynomial with at least one coefficient other than 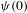 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D713}(0)$ an irrational number. We adapt an argument due to Furstenberg to prove that the sequence
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D713}(0)$ an irrational number. We adapt an argument due to Furstenberg to prove that the sequence 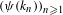 $(\unicode[STIX]{x1D713}(k_{n}))_{n\geq 1}$ is uniformly distributed modulo one. This is used to give some new families of Poincaré recurrent sequences. In addition we show these sequences are also intersective and Glasner.
$(\unicode[STIX]{x1D713}(k_{n}))_{n\geq 1}$ is uniformly distributed modulo one. This is used to give some new families of Poincaré recurrent sequences. In addition we show these sequences are also intersective and Glasner.
- Type
- Original Article
- Information
- Creative Commons
- This is an Open Access article, distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution licence (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted re-use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
- Copyright
- © Cambridge University Press, 2018


